 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
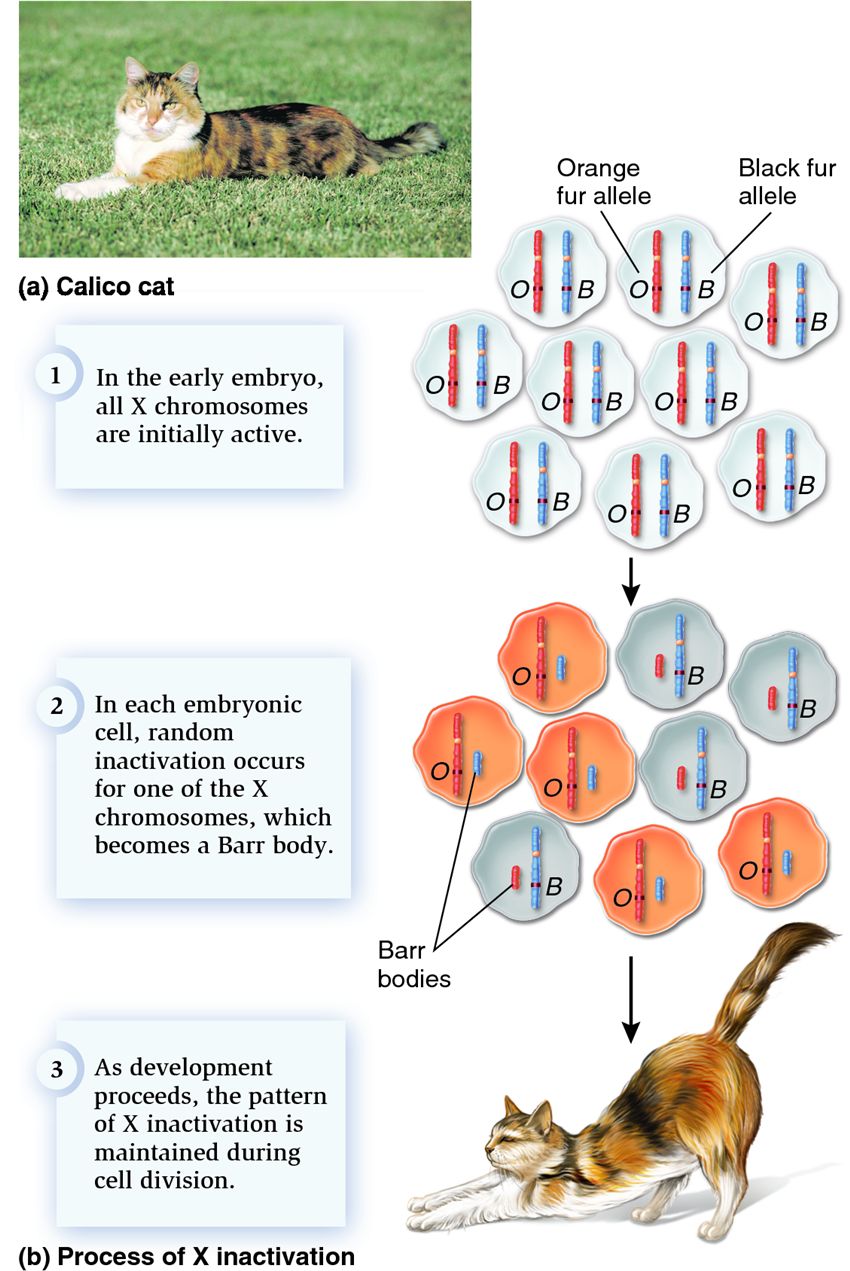
| Description: (a) A calico cat. (b) X inactivation during embryonic development. The calico pattern is due to random X-chromosome inactivation in a female that is heterozygous for the X-linked gene with black and orange alleles. The cells at the top of this figure represent a small mass of cells making up the very early embryo. In these cells, both X chromosomes are active. At an early stage of embryonic development, one X chromosome is randomly inactivated in each cell. The initial inactivation pattern is maintained in the descendents of each cell as the embryo matures into an adult. The pattern of orange and black fur in the adult cat reflects the pattern of X inactivation in the embryo.
Picture Stats: Views: 6527 Filesize: 152.63kB Height: 1271 Width: 850 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=539 Keywords: Random X-chromosome inactivation in a calico cat. |
