 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
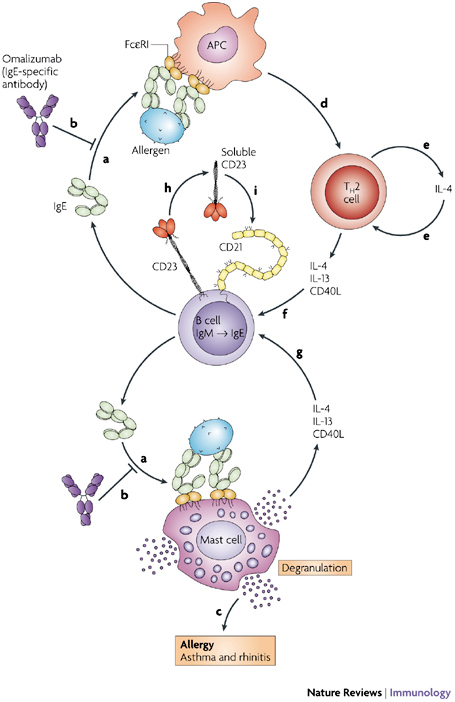
| Description: IgE is synthesized and secreted by B cells that have undergone heavy-chain class switching from IgM to IgE. The IgE binds to FcepsilonRI on mast cells and antigen-presenting cells (APCs) (a) and sensitizes these cells to allergens. Omalizumab inhibits the binding of IgE to FcepsilonRI on mast cells and APCs (b). Allergen binding to IgE triggers mast-cell degranulation to cause an allergic response (c). Allergen binding to the APC leads to the presentation of allergenic peptides to T helper 2 (TH2) cells (d). The allergen-activated TH2 cells secrete interleukin-4 (IL-4) (e) to maintain the TH2-cell lineage and recruit more TH cells into this lineage (e). The TH2 cells also secrete IL-13 and express CD40 ligand (CD40L), which together with IL-4 stimulates heavy-chain class switching to IgE (f). The allergen-activated mast cells contribute to the production of IL-4 and IL-13 (and express CD40L), which may also stimulate heavy-chain class switching to IgE (g). IL-4, IL-13 and CD40L also stimulate the expression of CD23 and the release of soluble CD23 (h). In humans, soluble trimeric CD23 upregulates IgE synthesis and secretion through interaction with CD21 (i). Thus, allergen acts in pump priming of the allergic response.
Picture Stats: Views: 1285 Filesize: 124.69kB Height: 702 Width: 455 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=8309 Keywords: Allergic response by allergens |
