|
|
|
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness. As of yet, there is no cure. Everyone is at risk, and there may be no warning signs. It is six to eight times more common in African Americans than in whites. The best and most effective way to detect glaucoma is to receive a dilated eye examination.
Only one in 10 cancer deaths is caused by the primary tumor. The vast majority of cancer mortality is caused by cells breaking away from the main tumor and metastasizing to other parts of the body, such as the brain, bones, or liver.
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.
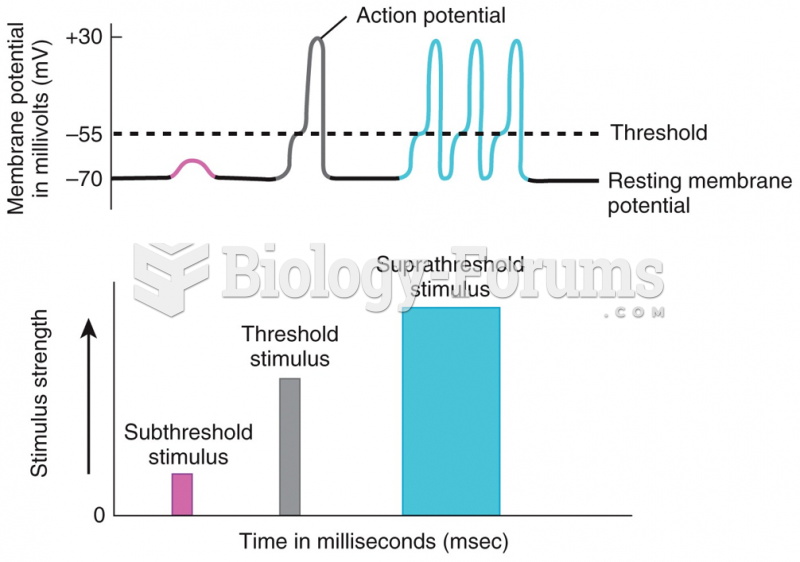
If all the neurons in the human body were lined up, they would stretch more than 600 miles.
The most common childhood diseases include croup, chickenpox, ear infections, flu, pneumonia, ringworm, respiratory syncytial virus, scabies, head lice, and asthma.
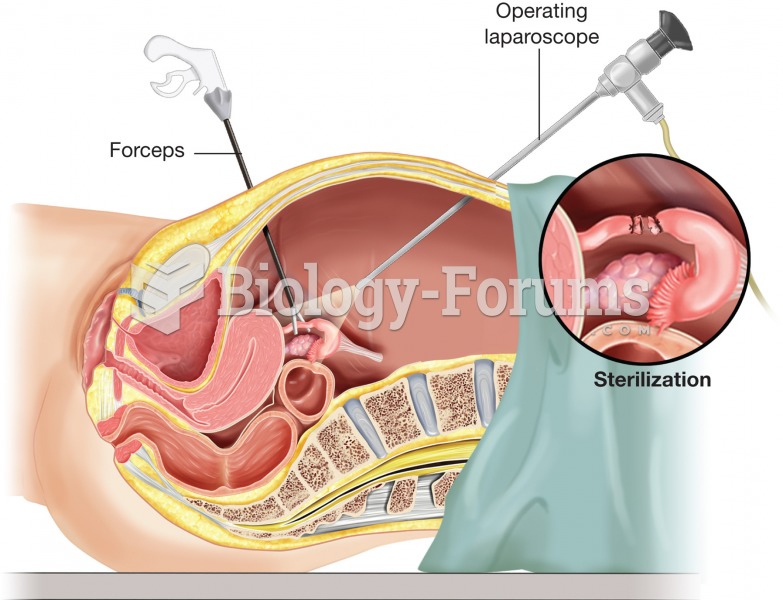 Tubal ligation. To minimize the size of the incisions necessary, laparoscopic surgery may be used to
Tubal ligation. To minimize the size of the incisions necessary, laparoscopic surgery may be used to
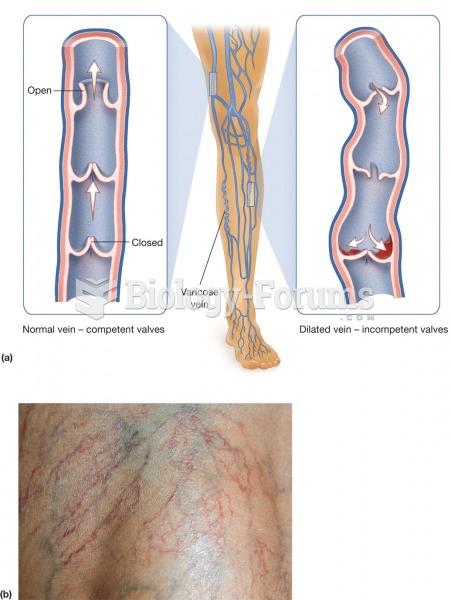 Varicosis. (a) Varicose veins develop due to the failure of valves in the superficial veins of the l
Varicosis. (a) Varicose veins develop due to the failure of valves in the superficial veins of the l