|
|
|
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
Between 1999 and 2012, American adults with high total cholesterol decreased from 18.3% to 12.9%
Hyperthyroidism leads to an increased rate of metabolism and affects about 1% of women but only 0.1% of men. For most people, this increased metabolic rate causes the thyroid gland to become enlarged (known as a goiter).
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis syndrome are life-threatening reactions that can result in death. Complications include permanent blindness, dry-eye syndrome, lung damage, photophobia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, permanent loss of nail beds, scarring of mucous membranes, arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Many patients' pores scar shut, causing them to retain heat.
Malaria mortality rates are falling. Increased malaria prevention and control measures have greatly improved these rates. Since 2000, malaria mortality rates have fallen globally by 60% among all age groups, and by 65% among children under age 5.
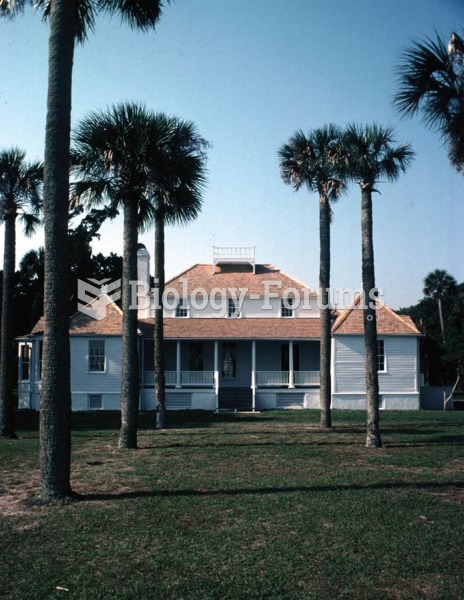 The Kingsley plantation, on Fort George Island in Jacksonville, Florida. Zephaniah Kingsley, the own
The Kingsley plantation, on Fort George Island in Jacksonville, Florida. Zephaniah Kingsley, the own
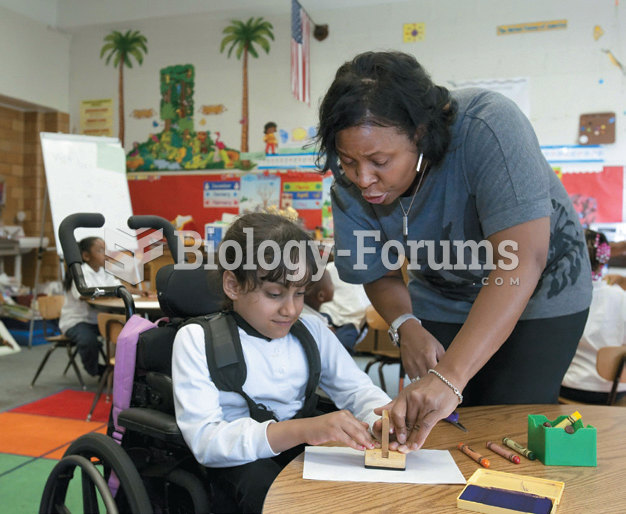 Children with disabilities used to be sent to special schools. In a process called mainstreaming or ...
Children with disabilities used to be sent to special schools. In a process called mainstreaming or ...