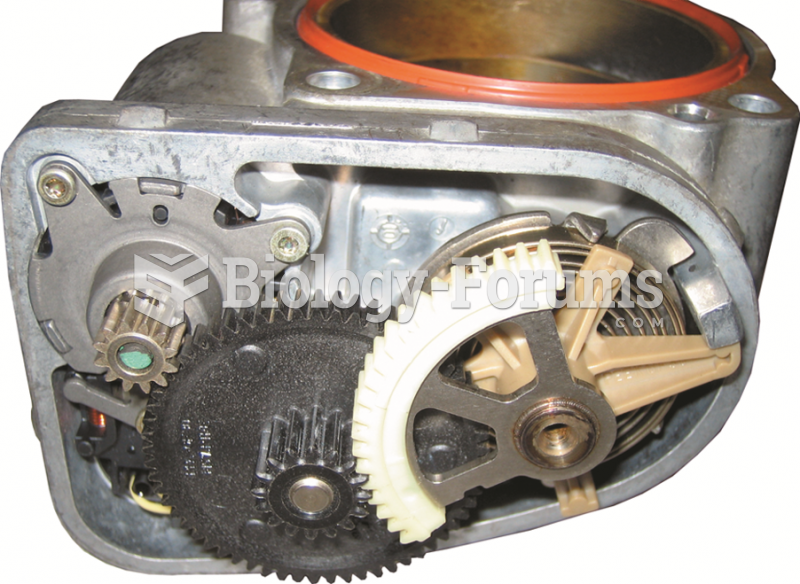
|
|
|
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
People with alcoholism are at a much greater risk of malnutrition than are other people and usually exhibit low levels of most vitamins (especially folic acid). This is because alcohol often takes the place of 50% of their daily intake of calories, with little nutritional value contained in it.
Sildenafil (Viagra®) has two actions that may be of consequence in patients with heart disease. It can lower the blood pressure, and it can interact with nitrates. It should never be used in patients who are taking nitrates.
More than one-third of adult Americans are obese. Diseases that kill the largest number of people annually, such as heart disease, cancer, diabetes, stroke, and hypertension, can be attributed to diet.
Although puberty usually occurs in the early teenage years, the world's youngest parents were two Chinese children who had their first baby when they were 8 and 9 years of age.