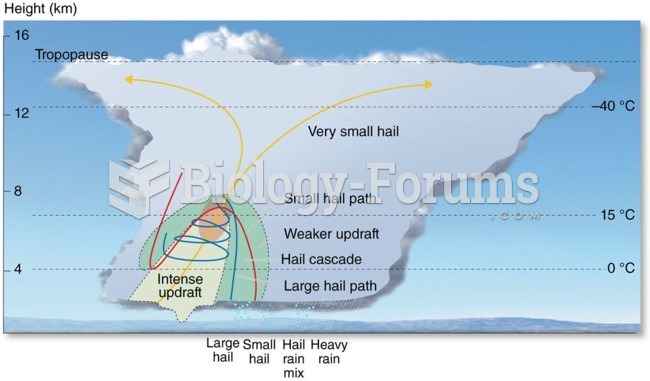
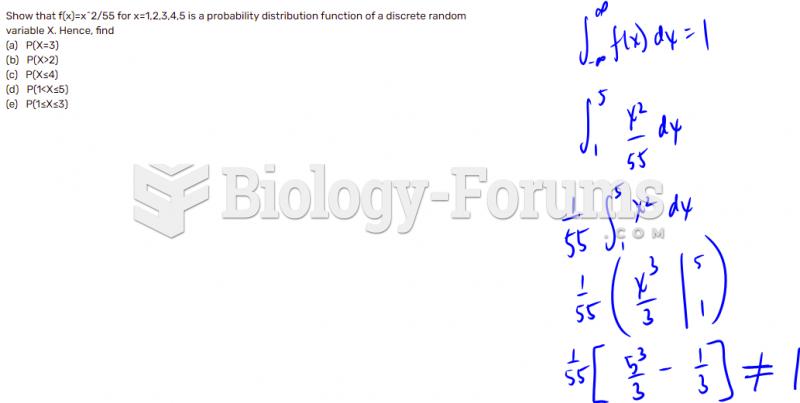
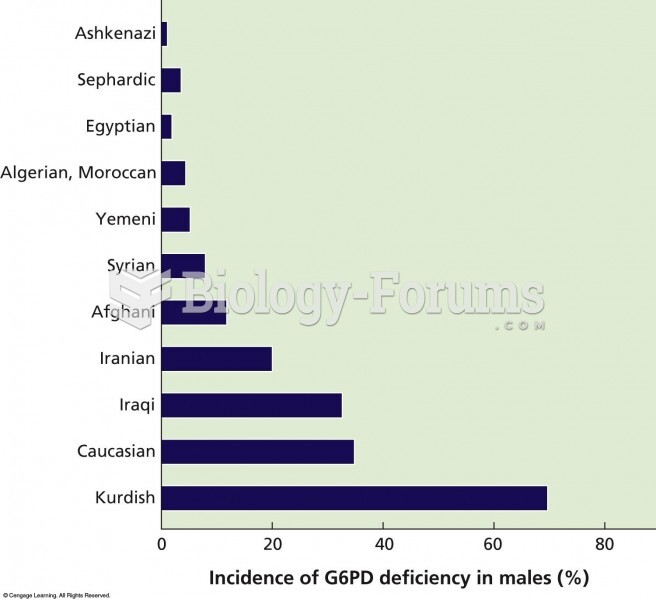
|
|
|
More than 30% of American adults, and about 12% of children utilize health care approaches that were developed outside of conventional medicine.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.
Certain topical medications such as clotrimazole and betamethasone are not approved for use in children younger than 12 years of age. They must be used very cautiously, as directed by a doctor, to treat any child. Children have a much greater response to topical steroid medications.
In 1885, the Lloyd Manufacturing Company of Albany, New York, promoted and sold "Cocaine Toothache Drops" at 15 cents per bottle! In 1914, the Harrison Narcotic Act brought the sale and distribution of this drug under federal control.