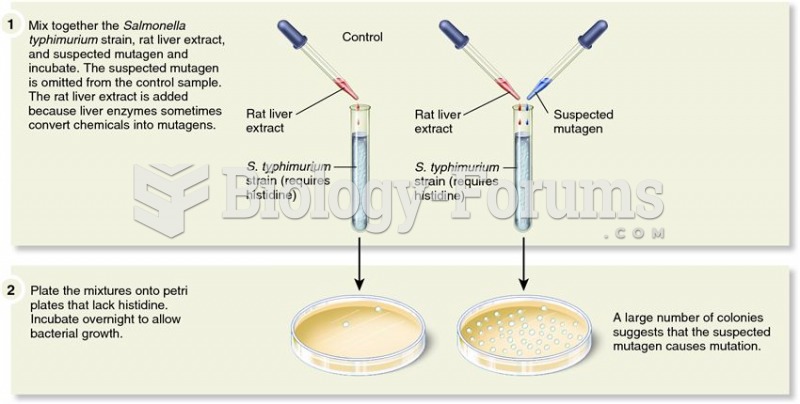
|
|
|
Your chance of developing a kidney stone is 1 in 10. In recent years, approximately 3.7 million people in the United States were diagnosed with a kidney disease.
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.
Many supplement containers do not even contain what their labels say. There are many documented reports of products containing much less, or more, that what is listed on their labels. They may also contain undisclosed prescription drugs and even contaminants.
Allergies play a major part in the health of children. The most prevalent childhood allergies are milk, egg, soy, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood.
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.