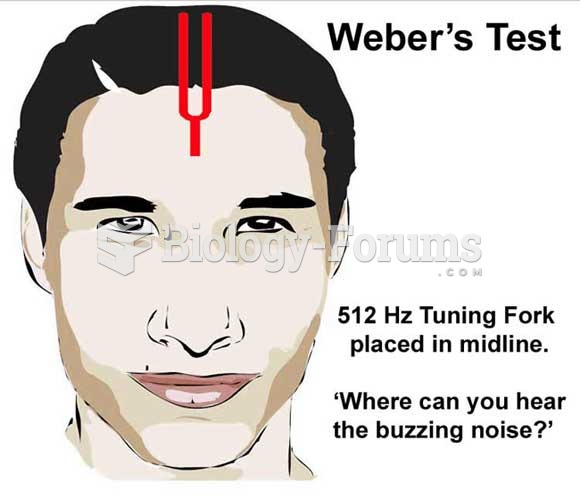
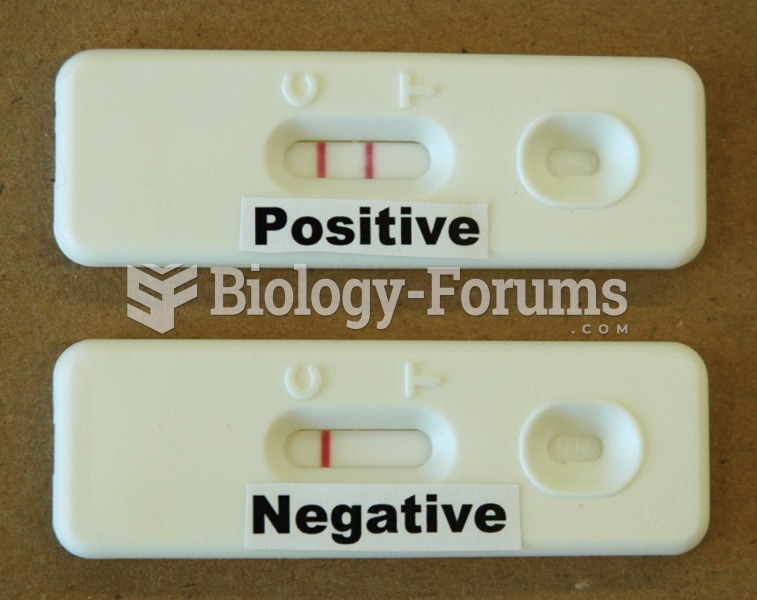
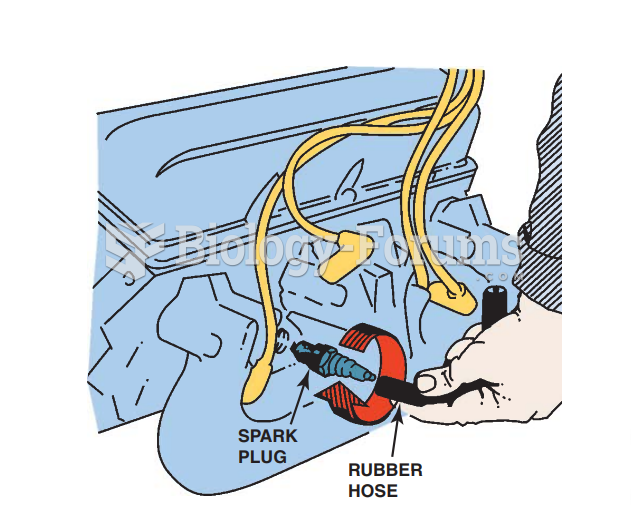
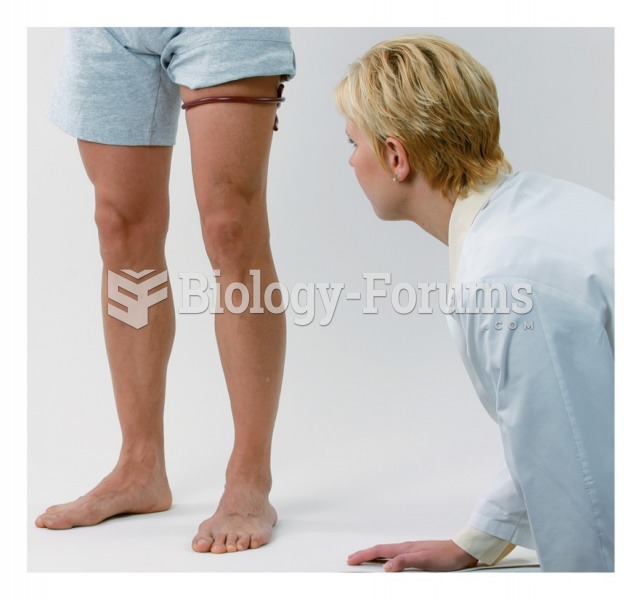
|
|
|
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA was discovered in 1961 in the United Kingdom. It if often referred to as a superbug. MRSA infections cause more deaths in the United States every year than AIDS.
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
Immunoglobulin injections may give short-term protection against, or reduce severity of certain diseases. They help people who have an inherited problem making their own antibodies, or those who are having certain types of cancer treatments.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
In 2010, opiate painkllers, such as morphine, OxyContin®, and Vicodin®, were tied to almost 60% of drug overdose deaths.