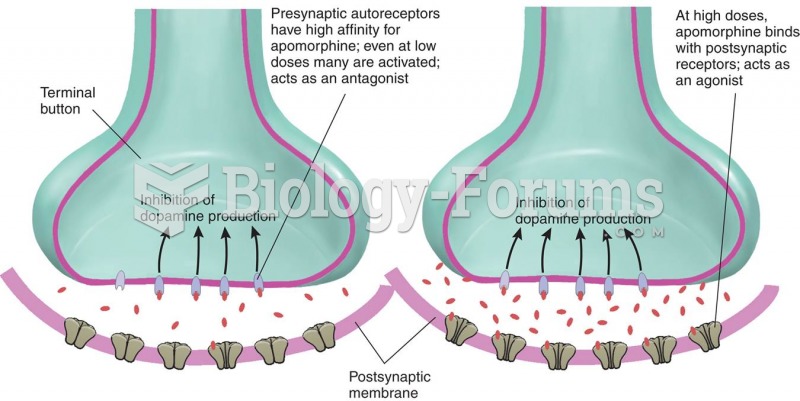
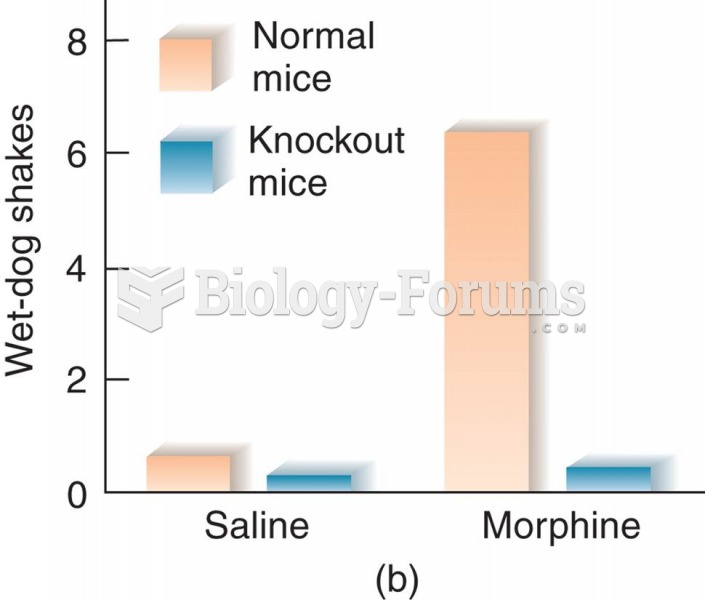
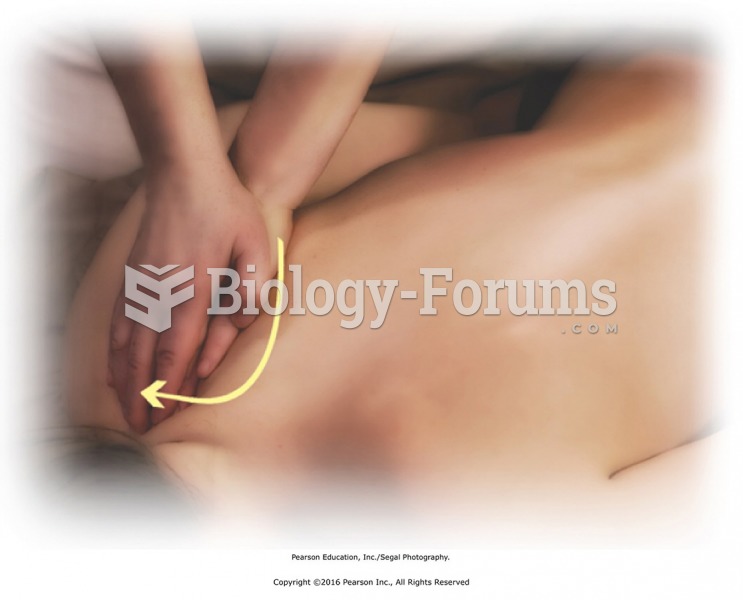
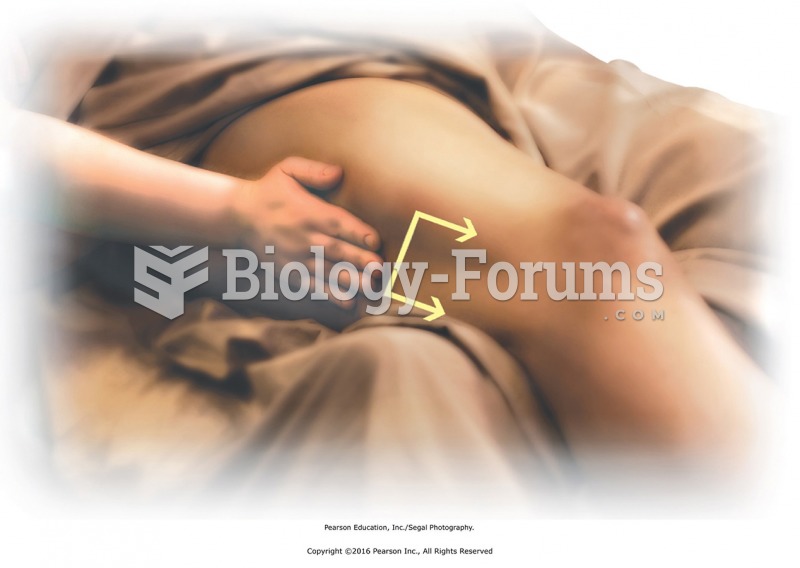
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.
Did you know?
More than 150,000 Americans killed by cardiovascular disease are younger than the age of 65 years.
Did you know?
The FDA recognizes 118 routes of administration.
Did you know?
Though “Krazy Glue” or “Super Glue” has the ability to seal small wounds, it is not recommended for this purpose since it contains many substances that should not enter the body through the skin, and may be harmful.
Did you know?
Throughout history, plants containing cardiac steroids have been used as heart drugs and as poisons (e.g., in arrows used in combat), emetics, and diuretics.