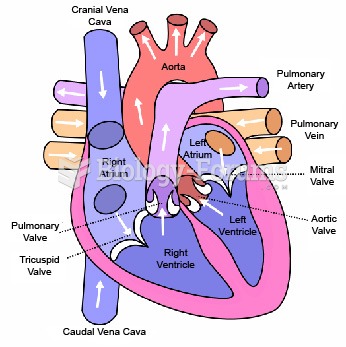
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
Did you know?
Oxytocin is recommended only for pregnancies that have a medical reason for inducing labor (such as eclampsia) and is not recommended for elective procedures or for making the birthing process more convenient.
Did you know?
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
Did you know?
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
Did you know?
Famous people who died from poisoning or drug overdose include, Adolf Hitler, Socrates, Juan Ponce de Leon, Marilyn Monroe, Judy Garland, and John Belushi.