|
|
|
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
Normal urine is sterile. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It is free of bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
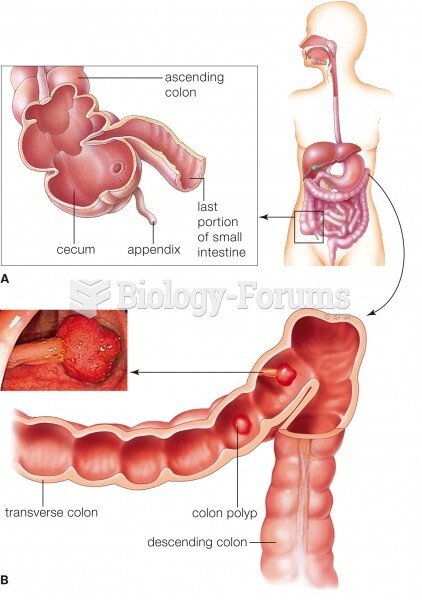
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.