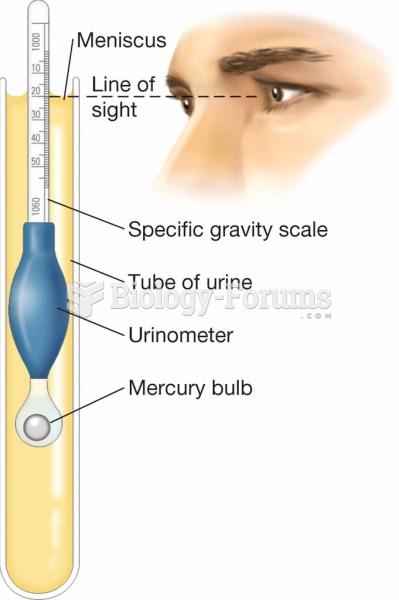
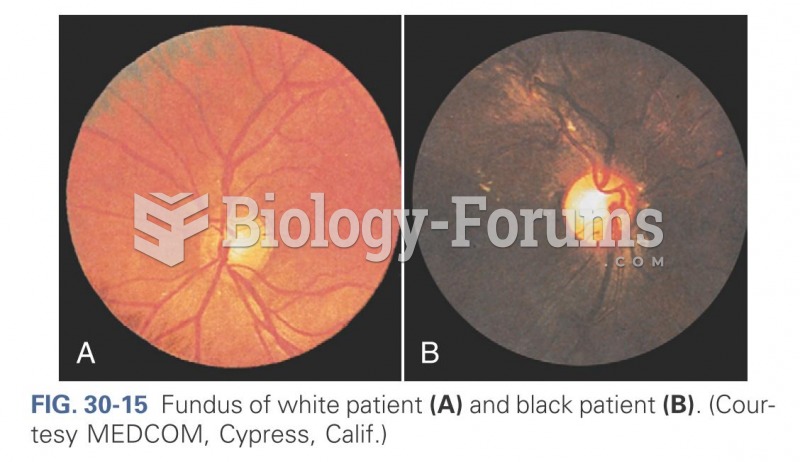
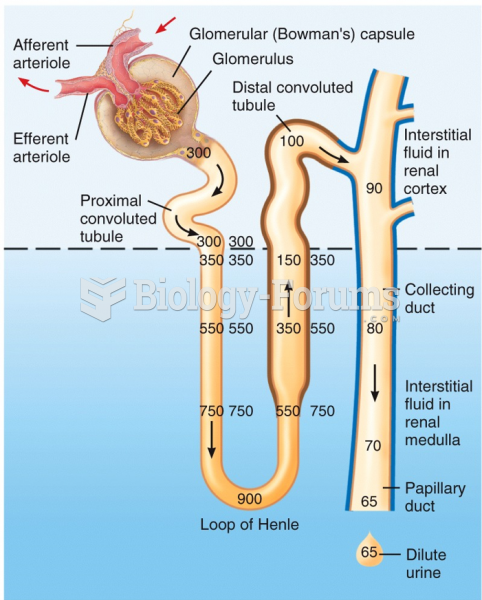
|
|
|
Colchicine is a highly poisonous alkaloid originally extracted from a type of saffron plant that is used mainly to treat gout.
The first war in which wide-scale use of anesthetics occurred was the Civil War, and 80% of all wounds were in the extremities.
Serum cholesterol testing in adults is recommended every 1 to 5 years. People with diabetes and a family history of high cholesterol should be tested even more frequently.
About 80% of major fungal systemic infections are due to Candida albicans. Another form, Candida peritonitis, occurs most often in postoperative patients. A rare disease, Candida meningitis, may follow leukemia, kidney transplant, other immunosuppressed factors, or when suffering from Candida septicemia.
The average older adult in the United States takes five prescription drugs per day. Half of these drugs contain a sedative. Alcohol should therefore be avoided by most senior citizens because of the dangerous interactions between alcohol and sedatives.