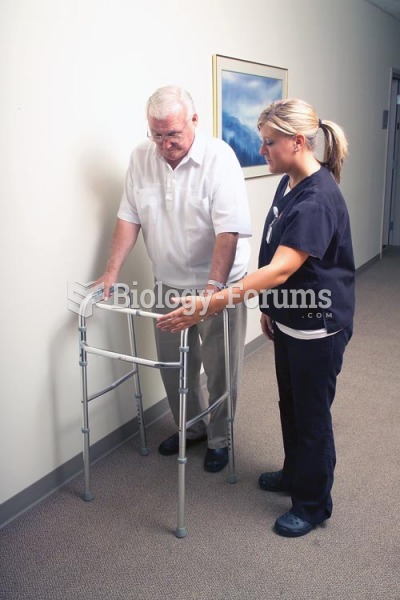
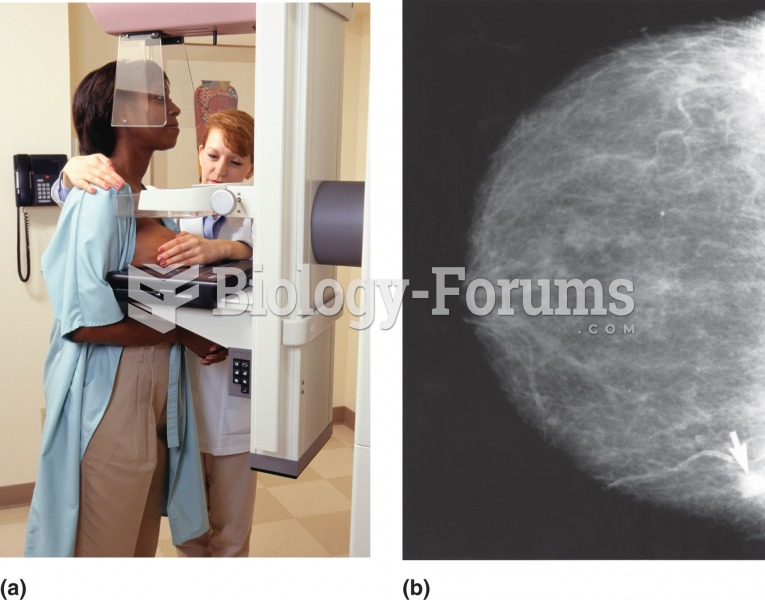
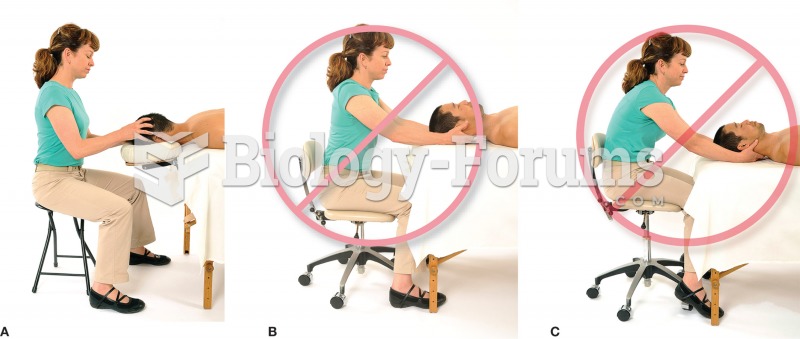
Answer to Question 1
B
Suspect tuberculosis (TB) in any patient with respiratory symptoms lasting longer than 3 weeks accompanied by other suspicious symptoms, such as unexplained weight loss, night sweats, fever, and a productive cough often streaked with blood. Isolation for patients with suspected or confirmed TB includes placing the patient on airborne precautions in a single-patient negative-pressure room. In addition to standard precautions, use contact precautions for patients known or suspected to have serious illnesses easily transmitted by direct patient contact or by contact with items in the patient's environment. Examples of such illnesses include gastrointestinal, respiratory, skin, or wound infection and colonization with multidrug-resistant bacteria judged by the infection control program as follows: (1) enteric with a low infectious dose or prolonged environmental survival, including Clostridium difficile, Escherichia coli, Shigella, hepatitis A, or rotavirus; (2) skin infections that are highly contagious or that may occur on dry skin, including diphtheria (cutaneous), herpes simplex virus (neonatal or mucocutaneous), impetigo, major (noncontained) abscesses, cellulitis, decubiti, pediculosis, scabies, staphylococcal furunculosis in infants and young children, or zoster; or (3) viral/hemorrhagic conjunctivitis or viral hemorrhagic infection (Ebola, Lassa, or Marburg). In addition to standard precautions, use droplet precautions for patients known or suspected to have serious illnesses transmitted by large particle droplets. Examples of such illnesses include invasive Haemophilus influenzae type b disease, including meningitis, pneumonia, epiglottitis, and sepsis; and invasive Neisseria meningitidis disease, including meningitis, pneumonia, and sepsis. Other serious bacterial respiratory infections spread by droplet transmission include diphtheria (pharyngeal), Mycoplasma pneumoniae, pertussis, pneumonic plague, streptococcal pharyngitis, pneumonia, and scarlet fever in infants and young children. Serious viral infections spread by droplet transmission include adenovirus, influenza, mumps, parvovirus B19, and rubella.
Answer to Question 2
A
Apply the gown first, making sure that it covers all outer garments. Pull sleeves down to the wrist. Tie securely at the neck and waist. Next, apply either a surgical mask or a fitted respirator around the mouth and nose. Goggles or a face shield is put on after the gown and mask are applied. Gloves are put on last.