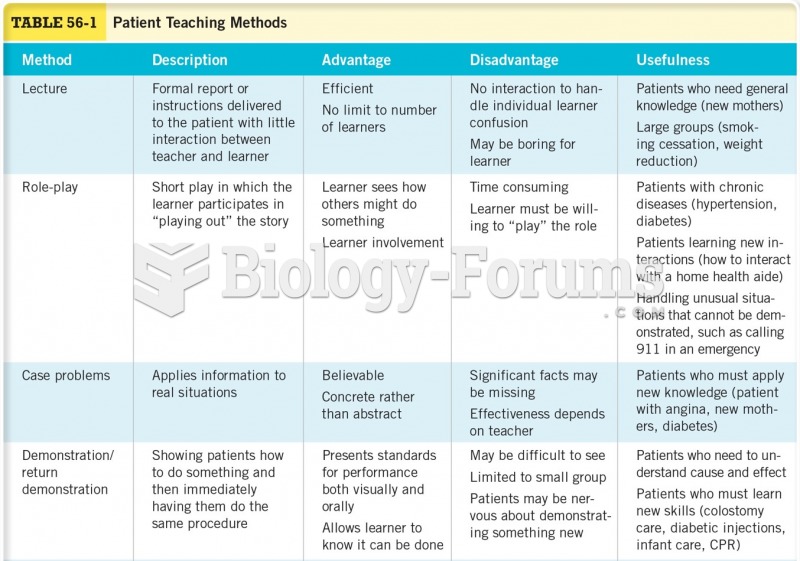
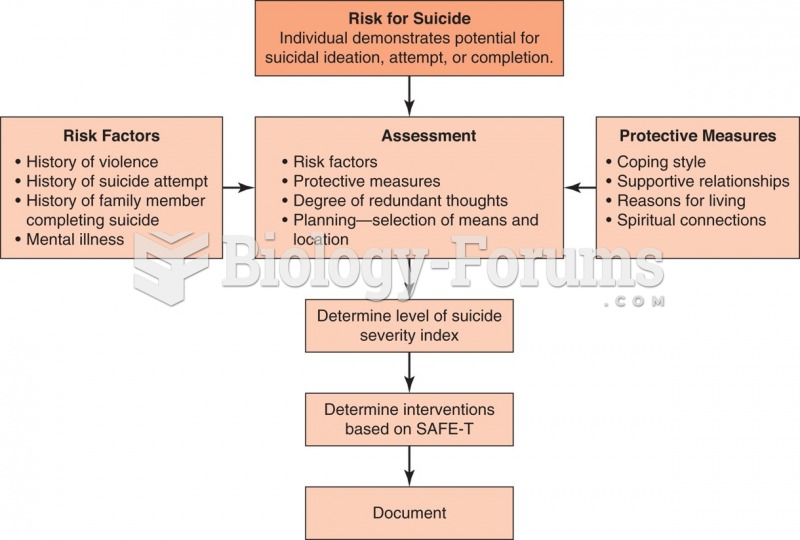
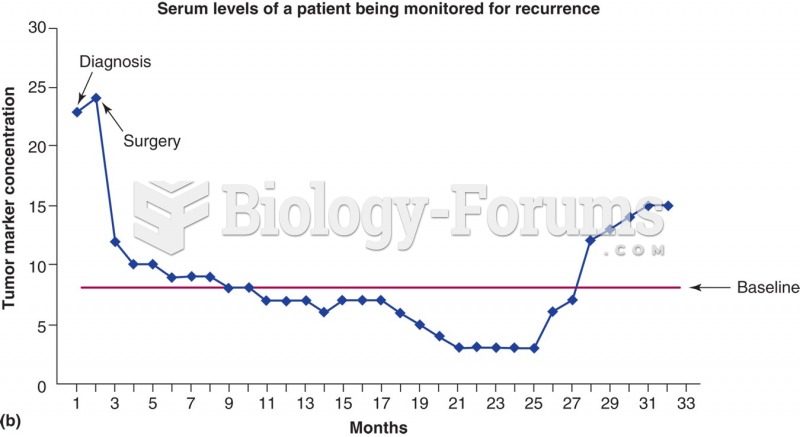
Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 1, 2, 3
Many patients with hearing deficits can read lips to some extent to assist in the communication process. Facing away from the patient does not alert the patient to the need to communicate. Offering alternative methods of communication allows for independence and clarity of communication if the patient chooses to use another method. The nurse allows the patient to maintain self-esteem and input to personal management. Facial gestures and hand gestures (nonverbal cues) contribute to communication; therefore, they are not distracting but helpful. Do not speak louder; use a deeper tone for better understanding, since higher pitch is lost first with most hearing problems. Do not use the same words, since consonants and vowels are not being understood. Try alternative words or methods of communication. Repeating the same words is frustrating for both persons.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 1
The patient should be instructed to avoid sudden changes in air pressure. No ear irrigations should be done during the postoperative as solution could enter through the tubes and contaminate the middle ear. Sterile swabs are not to be placed in the external canal because of the potential of dislodging the tubes, as well as the potential for middle ear contamination. Therefore, nothing should be inserted into the ear following surgery. A sterile cotton ball can be placed loosely at the external opening of the ear, not in the canal or near the tympanic membrane, to collect any drainage, but it should not be packed deeply into the ear canal. Swimming, submerging in water, and getting water in the ear are contraindicated for several months (not weeks) due to the risk of water contamination in the middle ear.