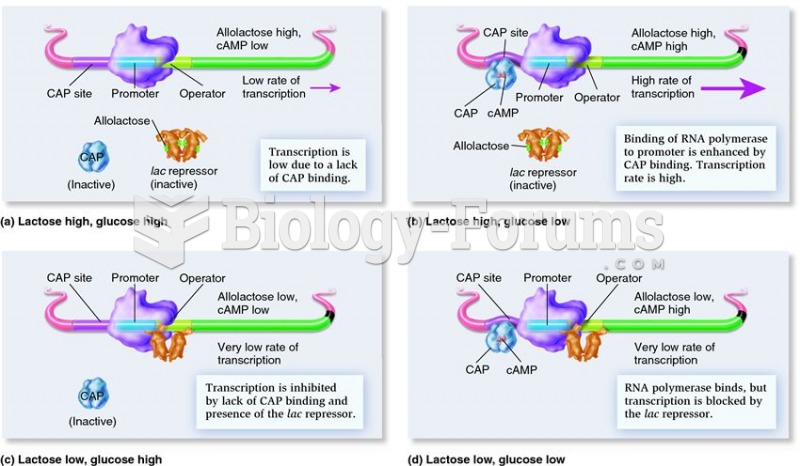
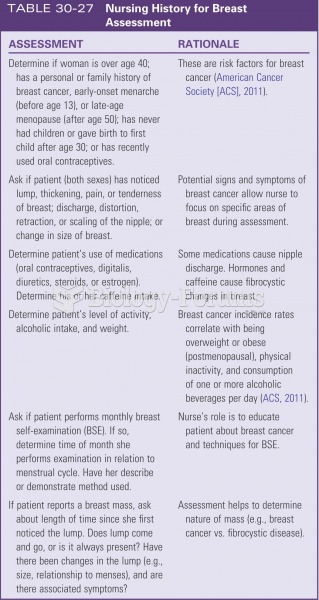
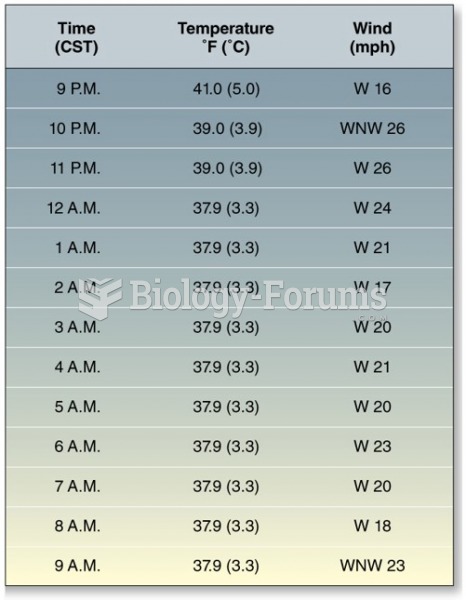
|
|
|
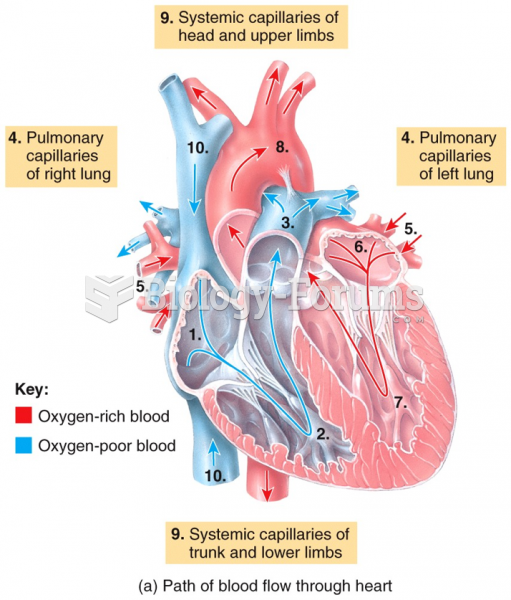
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
Hip fractures are the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. The incidence of hip fractures increases with each decade among patients in their 60s to patients in their 90s for both women and men of all populations. Men and women older than 80 years of age show the highest incidence of hip fractures.
Increased intake of vitamin D has been shown to reduce fractures up to 25% in older people.
Since 1988, the CDC has reported a 99% reduction in bacterial meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae, due to the introduction of the vaccine against it.
Throughout history, plants containing cardiac steroids have been used as heart drugs and as poisons (e.g., in arrows used in combat), emetics, and diuretics.