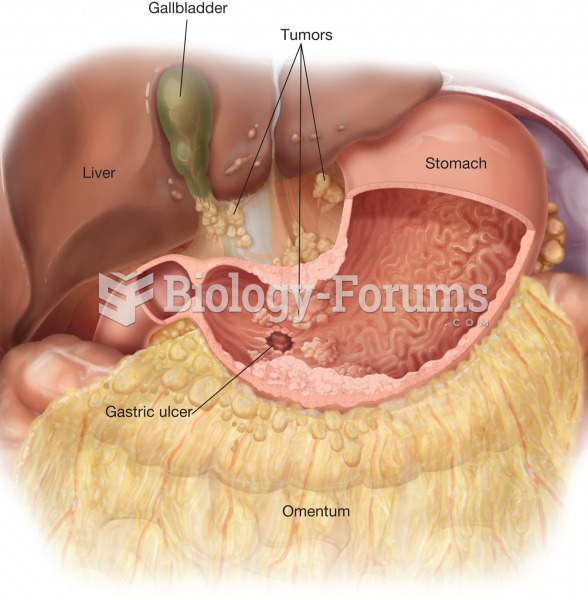
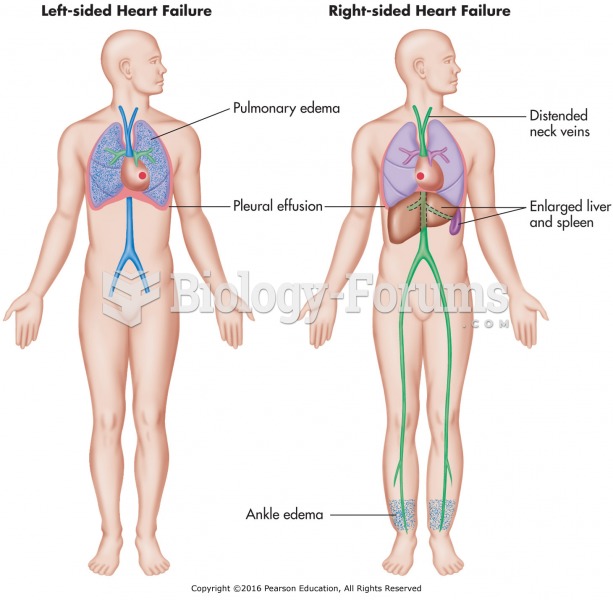
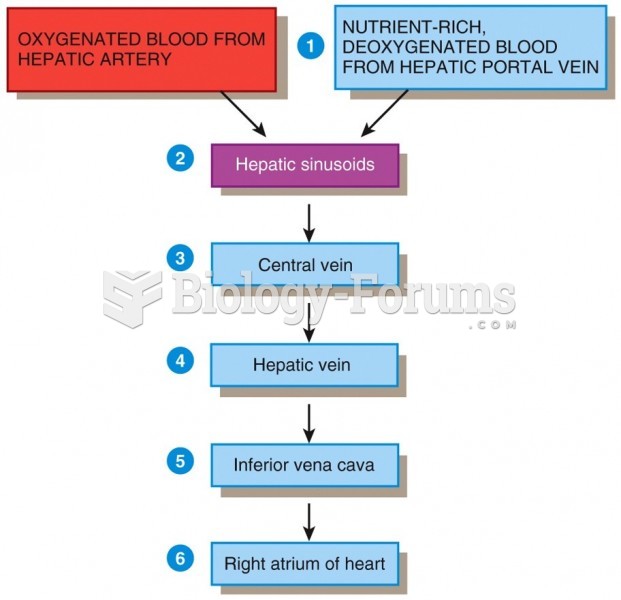
|
|
|
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
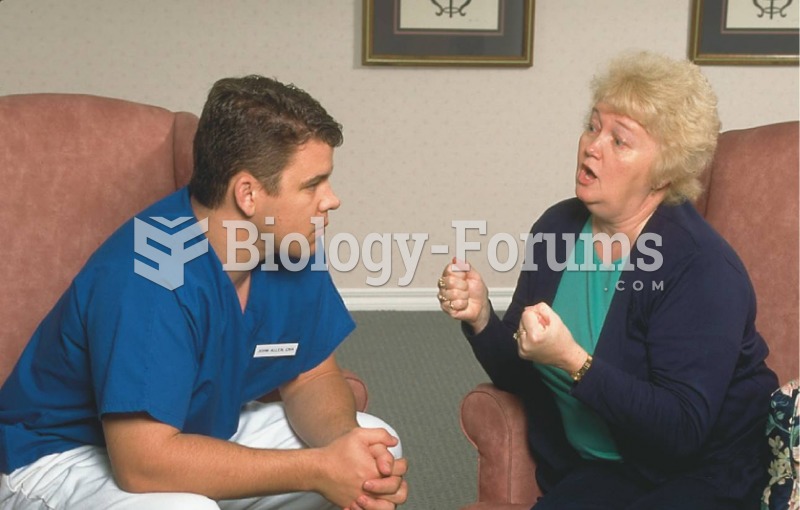
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.
Coca-Cola originally used coca leaves and caffeine from the African kola nut. It was advertised as a therapeutic agent and "pickerupper." Eventually, its formulation was changed, and the coca leaves were removed because of the effects of regulation on cocaine-related products.
Calcitonin is a naturally occurring hormone. In women who are at least 5 years beyond menopause, it slows bone loss and increases spinal bone density.
During the twentieth century, a variant of the metric system was used in Russia and France in which the base unit of mass was the tonne. Instead of kilograms, this system used millitonnes (mt).