|
|
|
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
Many people have small pouches in their colons that bulge outward through weak spots. Each pouch is called a diverticulum. About 10% of Americans older than age 40 years have diverticulosis, which, when the pouches become infected or inflamed, is called diverticulitis. The main cause of diverticular disease is a low-fiber diet.
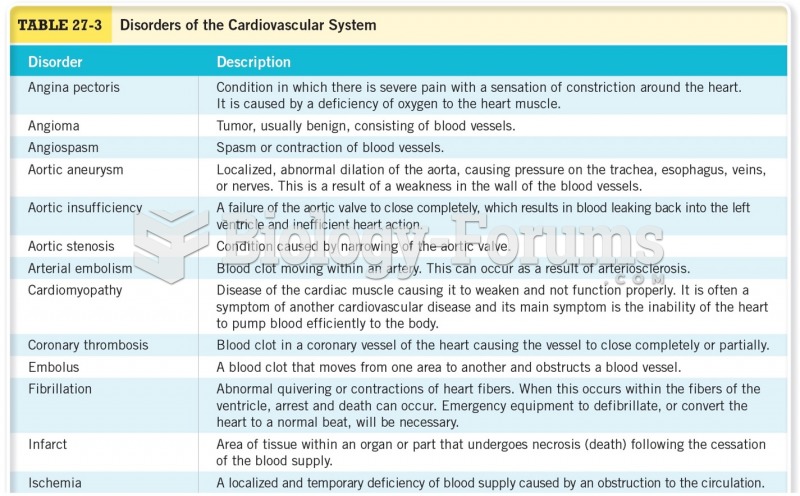
Most strokes are caused when blood clots move to a blood vessel in the brain and block blood flow to that area. Thrombolytic therapy can be used to dissolve the clot quickly. If given within 3 hours of the first stroke symptoms, this therapy can help limit stroke damage and disability.
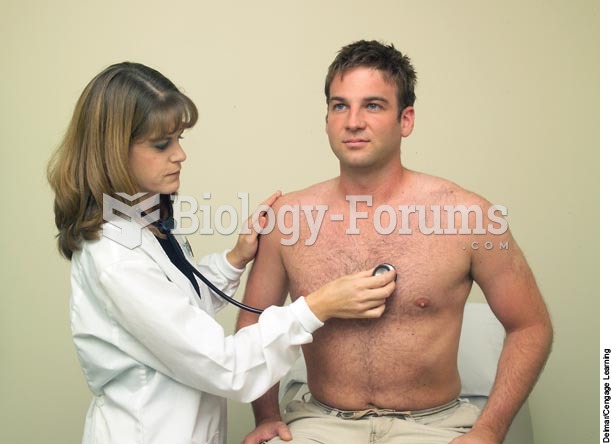
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.