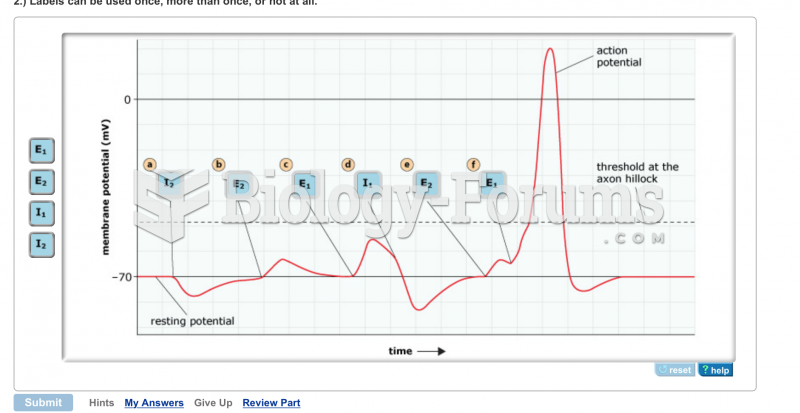
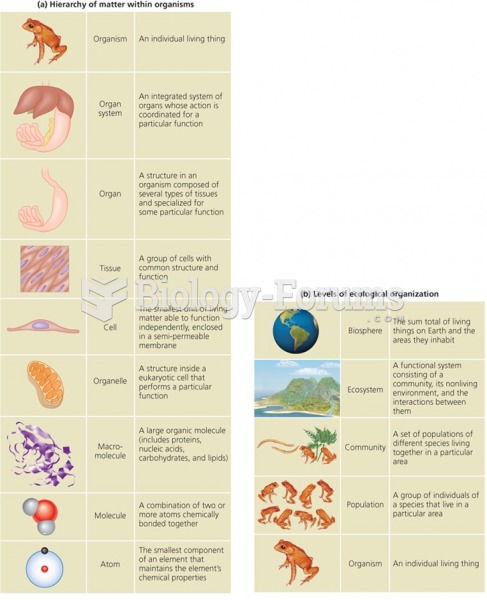
|
|
|
Did you know?
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
Did you know?
The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen in water (H2O) is 2:1.
Did you know?
To prove that stomach ulcers were caused by bacteria and not by stress, a researcher consumed an entire laboratory beaker full of bacterial culture. After this, he did indeed develop stomach ulcers, and won the Nobel Prize for his discovery.
Did you know?
The horizontal fraction bar was introduced by the Arabs.
Did you know?
When blood is deoxygenated and flowing back to the heart through the veins, it is dark reddish-blue in color. Blood in the arteries that is oxygenated and flowing out to the body is bright red. Whereas arterial blood comes out in spurts, venous blood flows.