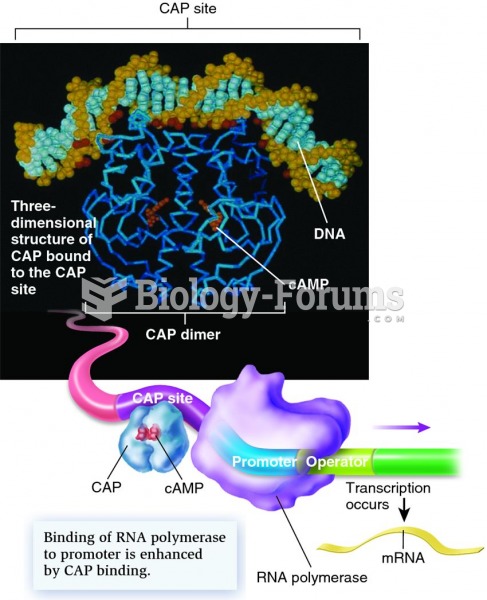
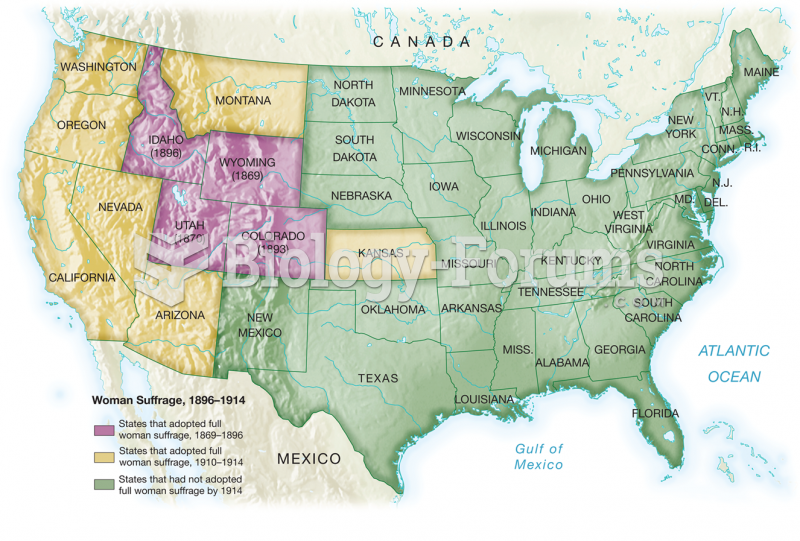
|
|
|
Did you know?
Anti-aging claims should not ever be believed. There is no supplement, medication, or any other substance that has been proven to slow or stop the aging process.
Did you know?
Barbituric acid, the base material of barbiturates, was first synthesized in 1863 by Adolph von Bayer. His company later went on to synthesize aspirin for the first time, and Bayer aspirin is still a popular brand today.
Did you know?
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.
Did you know?
The calories found in one piece of cherry cheesecake could light a 60-watt light bulb for 1.5 hours.
Did you know?
Less than one of every three adults with high LDL cholesterol has the condition under control. Only 48.1% with the condition are being treated for it.