|
|
|
The average adult has about 21 square feet of skin.
Never take aspirin without food because it is likely to irritate your stomach. Never give aspirin to children under age 12. Overdoses of aspirin have the potential to cause deafness.
Drug abusers experience the following scenario: The pleasure given by their drug (or drugs) of choice is so strong that it is difficult to eradicate even after years of staying away from the substances involved. Certain triggers may cause a drug abuser to relapse. Research shows that long-term drug abuse results in significant changes in brain function that persist long after an individual stops using drugs. It is most important to realize that the same is true of not just illegal substances but alcohol and tobacco as well.
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Patients who have been on total parenteral nutrition for more than a few days may need to have foods gradually reintroduced to give the digestive tract time to start working again.
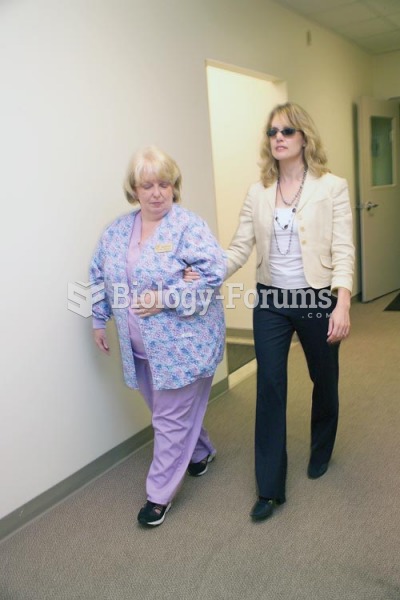 The nurse needs to inform the patient with impaired vision when a touch is to occur and ask permissi
The nurse needs to inform the patient with impaired vision when a touch is to occur and ask permissi
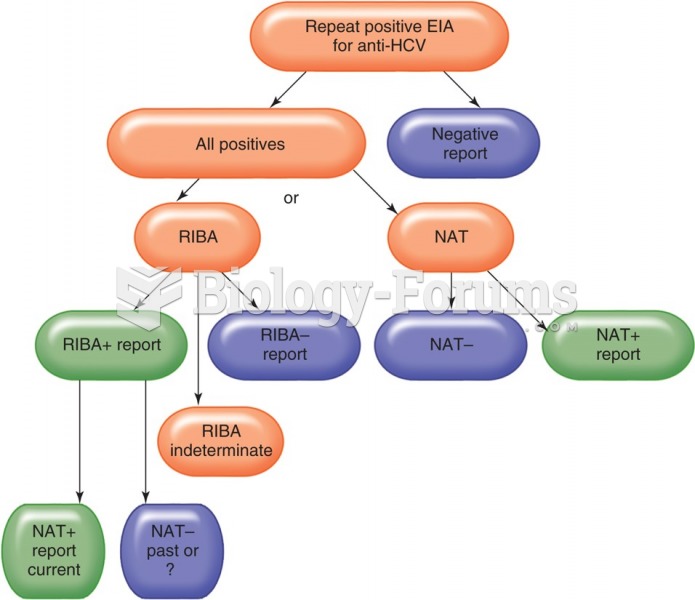
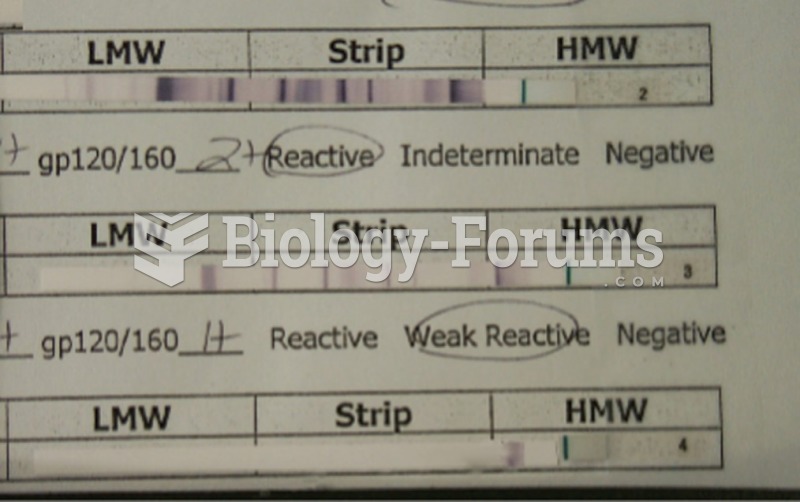 A Western blot for confirmatory HIV diagnosis. After an enzyme immunoassay has been performed and ...
A Western blot for confirmatory HIV diagnosis. After an enzyme immunoassay has been performed and ...