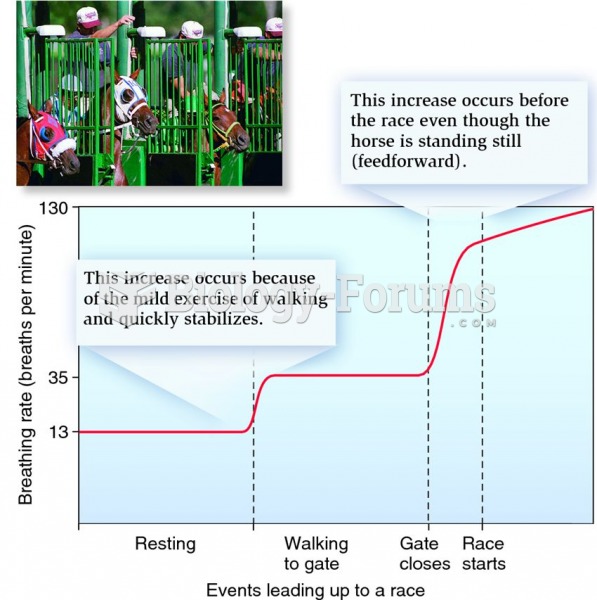
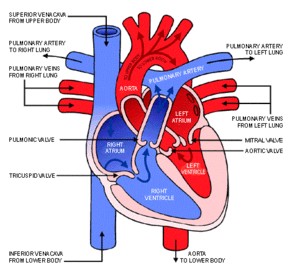
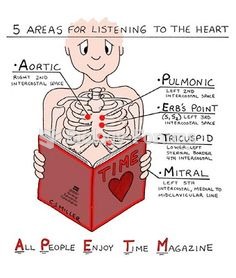
|
|
|
A headache when you wake up in the morning is indicative of sinusitis. Other symptoms of sinusitis can include fever, weakness, tiredness, a cough that may be more severe at night, and a runny nose or nasal congestion.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all women age 65 years of age or older should be screened with bone densitometry.
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates's recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.
More than 34,000 trademarked medication names and more than 10,000 generic medication names are in use in the United States.
Approximately 500,000 babies are born each year in the United States to teenage mothers.