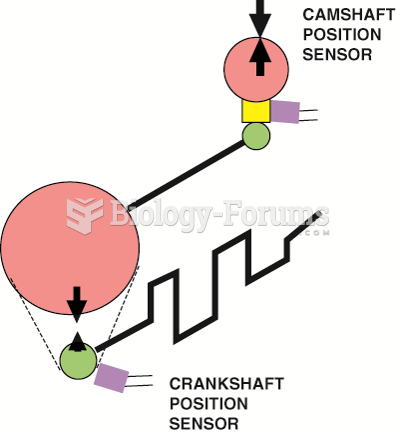
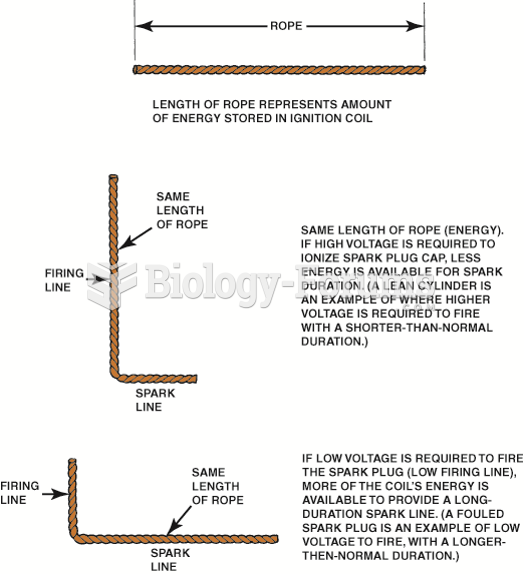
|
|
|
If all the neurons in the human body were lined up, they would stretch more than 600 miles.
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.
A serious new warning has been established for pregnant women against taking ACE inhibitors during pregnancy. In the study, the risk of major birth defects in children whose mothers took ACE inhibitors during the first trimester was nearly three times higher than in children whose mothers didn't take ACE inhibitors. Physicians can prescribe alternative medications for pregnant women who have symptoms of high blood pressure.
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.