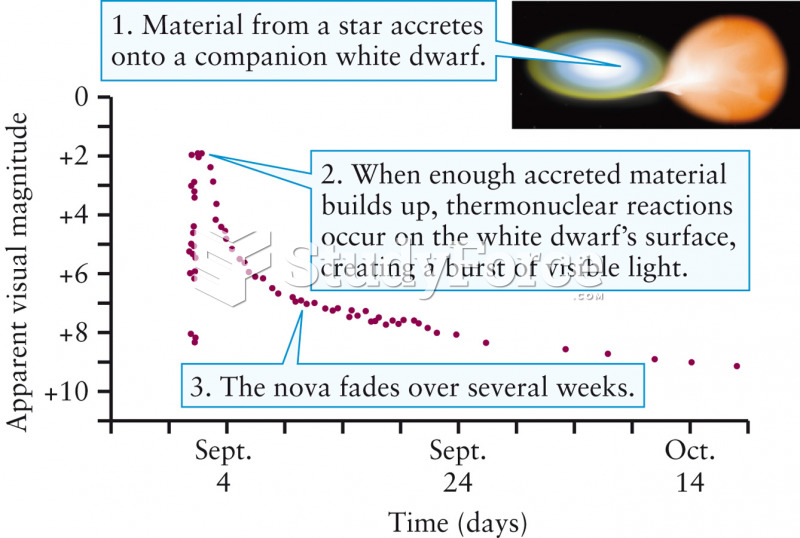
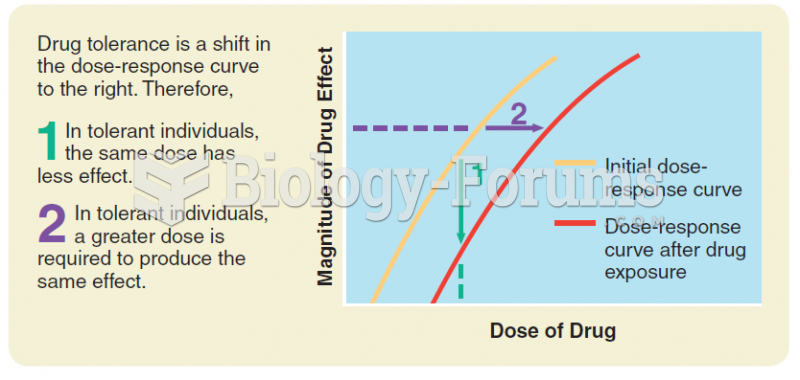
|
|
|
Though the United States has largely rejected the metric system, it is used for currency, as in 100 pennies = 1 dollar. Previously, the British currency system was used, with measurements such as 12 pence to the shilling, and 20 shillings to the pound.
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
Multiple experimental evidences have confirmed that at the molecular level, cancer is caused by lesions in cellular DNA.
Approximately 25% of all reported medication errors result from some kind of name confusion.
Dogs have been used in studies to detect various cancers in human subjects. They have been trained to sniff breath samples from humans that were collected by having them breathe into special tubes. These people included 55 lung cancer patients, 31 breast cancer patients, and 83 cancer-free patients. The dogs detected 54 of the 55 lung cancer patients as having cancer, detected 28 of the 31 breast cancer patients, and gave only three false-positive results (detecting cancer in people who didn't have it).
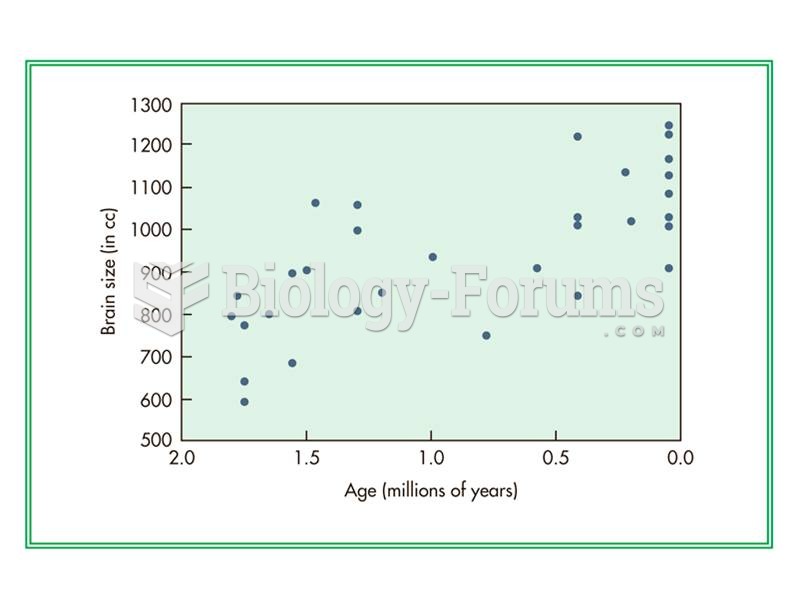 Although average brain size increases gradually though time in H. erectus, individuals with small br
Although average brain size increases gradually though time in H. erectus, individuals with small br
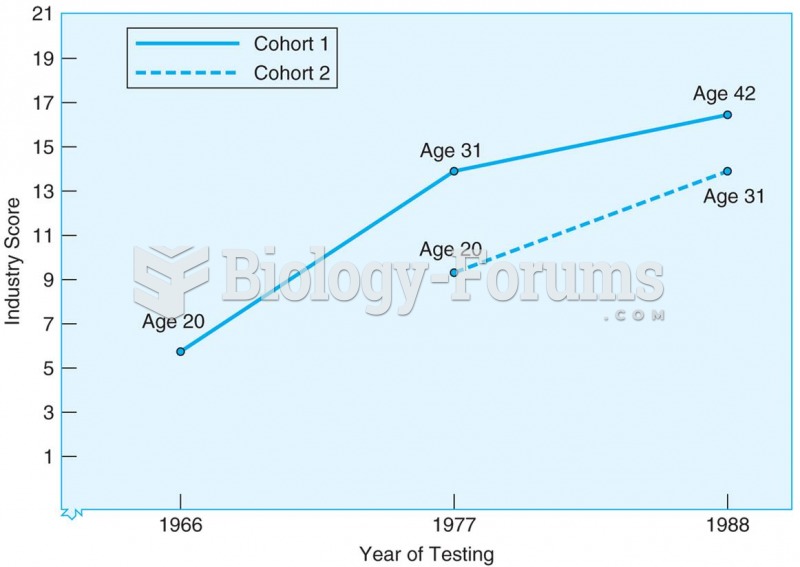 Results from sequential study of two cohorts tested at three ages and at three different points in t
Results from sequential study of two cohorts tested at three ages and at three different points in t