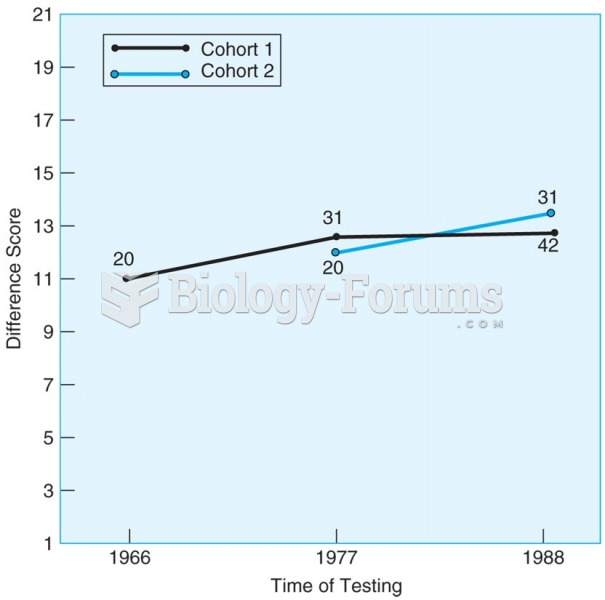
Answer to Question 1
An increase in the nominal money supply raises the real money supply, lowering the interest rate in the short run (the movement from 1 to 2 on the lower left figure). The money supply increase is considered to continue in the future, and thus it will affect the exchange rate expectations. This will make the expected return on the euro more desirable and thus the dollar depreciates. In the case of a permanent increase in the U.S. money supply, the dollar depreciates more than under a temporary increase in the money supply (from point to point in the upper left figure).
Now, in the long run, (the right hand side figure), prices will rise until the real money balances are the same as before the permanent increase in the money supply (from point 2 to point 4, in the lower right figure). Since the output level is given, the U.S. interest rate which decreased before, will start to increase, until it will move back to its original level (from Point 2 to 4 in the lower left figure). The equilibrium interest rate must be the same as its original long run value (at point 4 in the lower right figure). This increase in the interest rate must cause the dollar to appreciate against the euro after its sharp depreciation as a result of the permanent increase in the money supply (this process is depicted in the upper right figure from point to ). So a large depreciation (from Point in the left upper figure to pint in both the left and right upper figures) is followed by an appreciation of the dollar (the movement from to point in the upper right hand side figure). Eventually, the dollar depreciates in proportion to the increase in the price level, which in turn increases by the same proportion as the permanent increase in the money supply. Thus, money is neutral, in the sense that it cannot affect in the long run real variables, such as output, investment, etc. Note that points and represent the same exchange rate.
Answer to Question 2
E