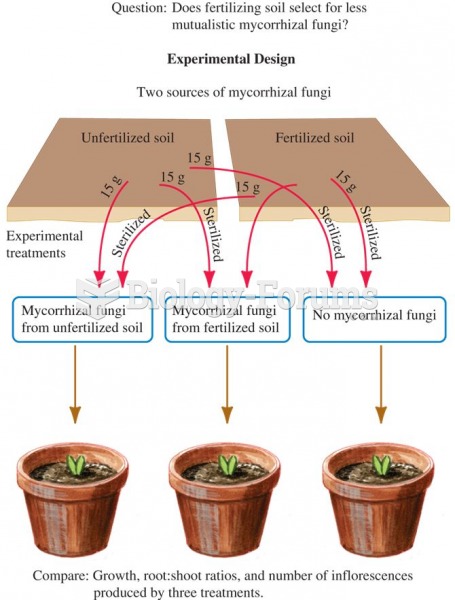
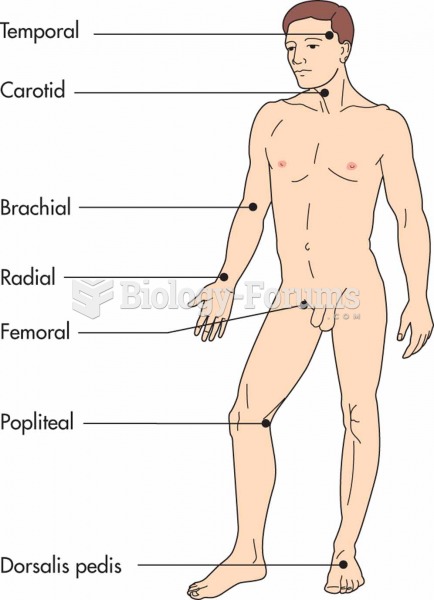
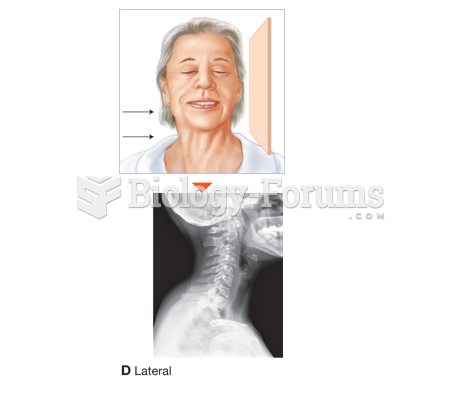
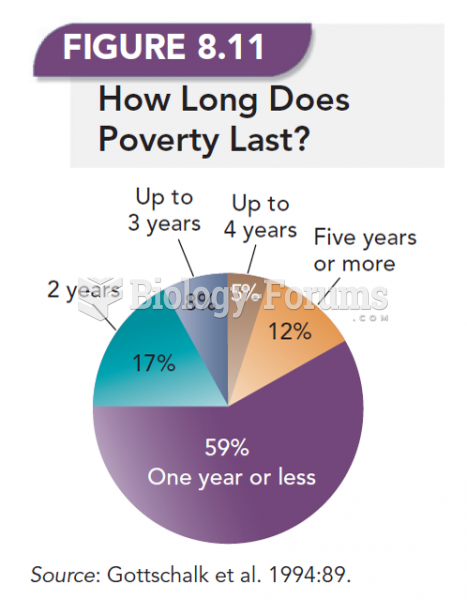
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
People often find it difficult to accept the idea that bacteria can be beneficial and improve health. Lactic acid bacteria are good, and when eaten, these bacteria improve health and increase longevity. These bacteria included in foods such as yogurt.
Did you know?
There are more sensory neurons in the tongue than in any other part of the body.
Did you know?
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
Did you know?
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.
Did you know?
Multiple experimental evidences have confirmed that at the molecular level, cancer is caused by lesions in cellular DNA.