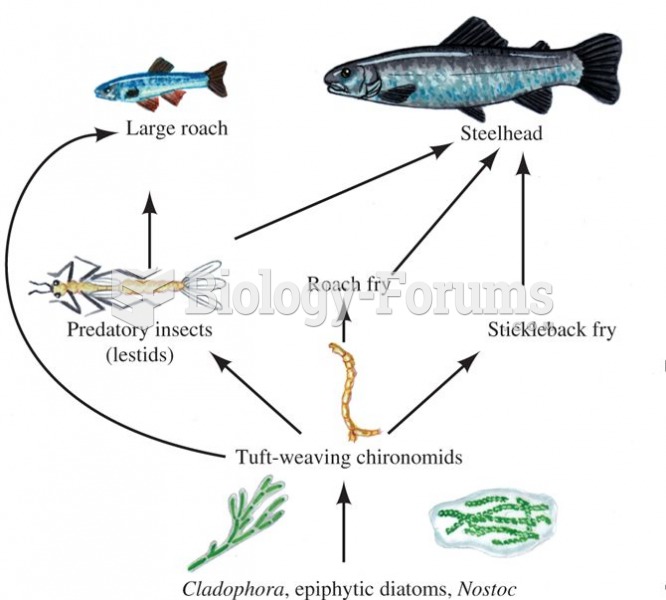
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The first oncogene was discovered in 1970 and was termed SRC (pronounced "SARK").
Did you know?
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
Did you know?
Women are 50% to 75% more likely than men to experience an adverse drug reaction.
Did you know?
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
Did you know?
The horizontal fraction bar was introduced by the Arabs.
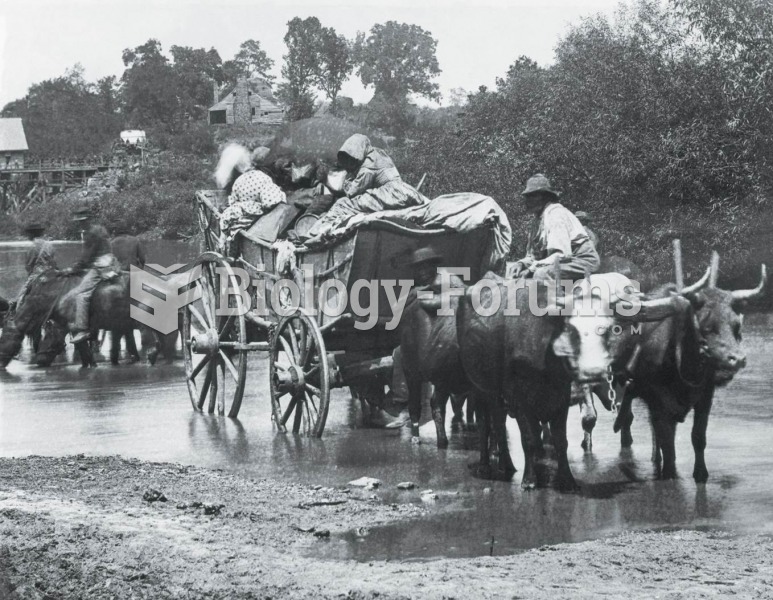 When Union troops pushed toward Richmond in June of 1862, these slaves crossed the Rappahannock Rive
When Union troops pushed toward Richmond in June of 1862, these slaves crossed the Rappahannock Rive
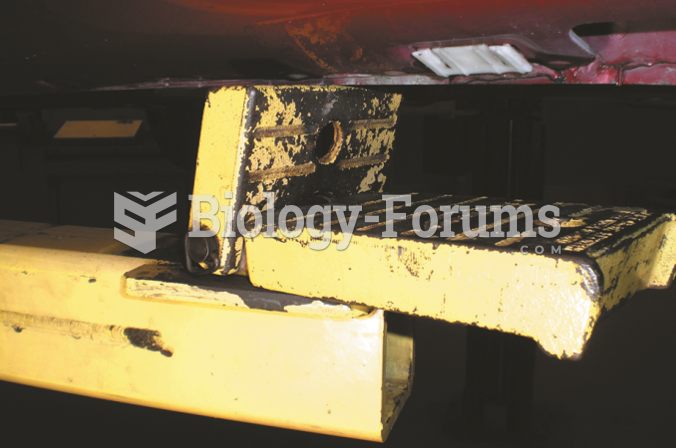 If raising a vehicle without a frame, place the flat pads under the pinch weld seam to spread the ...
If raising a vehicle without a frame, place the flat pads under the pinch weld seam to spread the ...