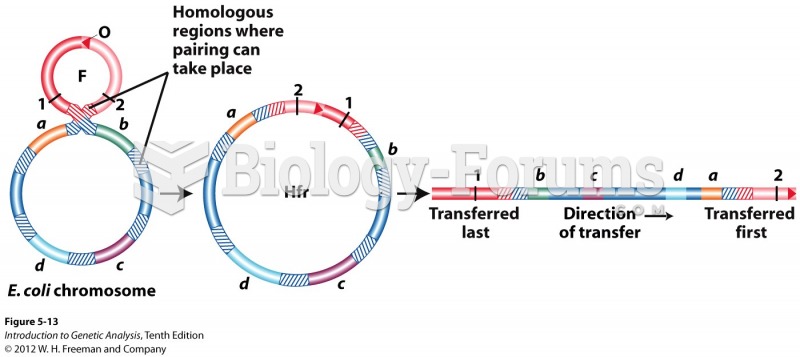
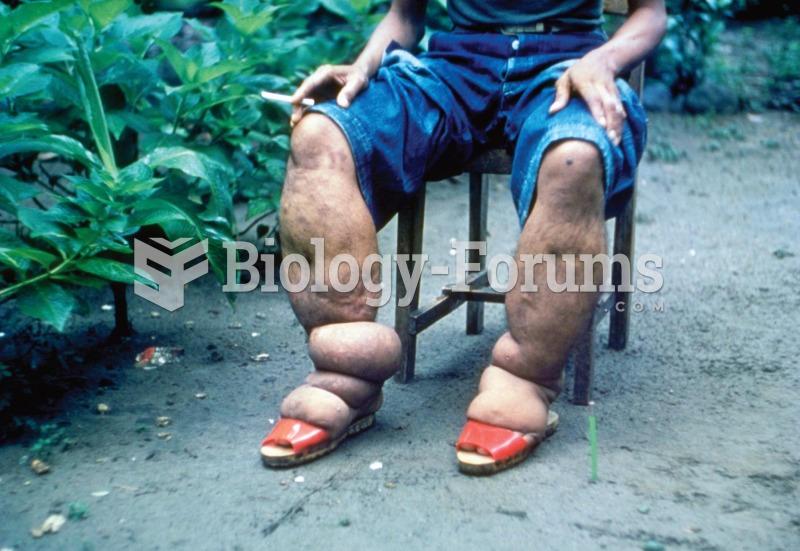
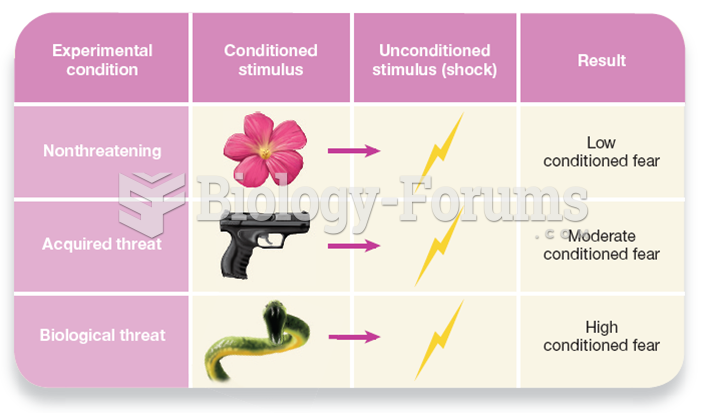
|
|
|
More than 150,000 Americans killed by cardiovascular disease are younger than the age of 65 years.
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.
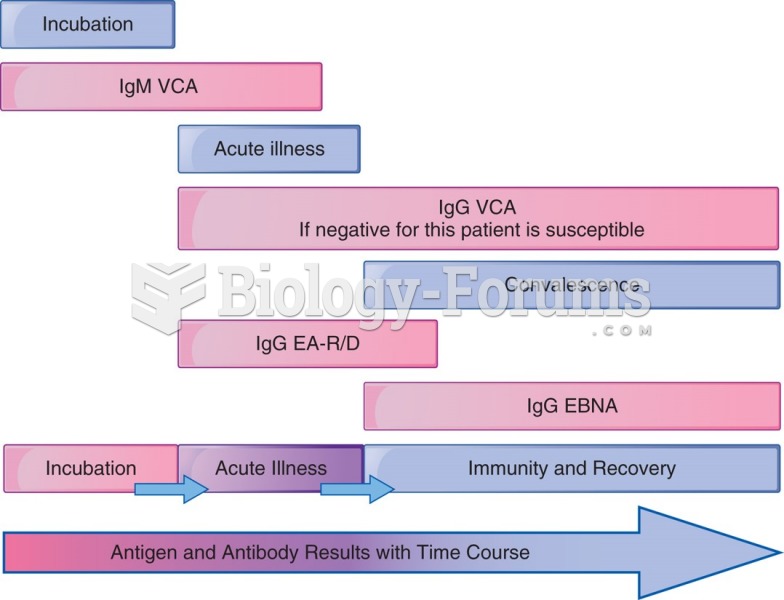
IgA antibodies protect body surfaces exposed to outside foreign substances. IgG antibodies are found in all body fluids. IgM antibodies are the first type of antibody made in response to an infection. IgE antibody levels are often high in people with allergies. IgD antibodies are found in tissues lining the abdomen and chest.
To combat osteoporosis, changes in lifestyle and diet are recommended. At-risk patients should include 1,200 to 1,500 mg of calcium daily either via dietary means or with supplements.
Pubic lice (crabs) are usually spread through sexual contact. You cannot catch them by using a public toilet.