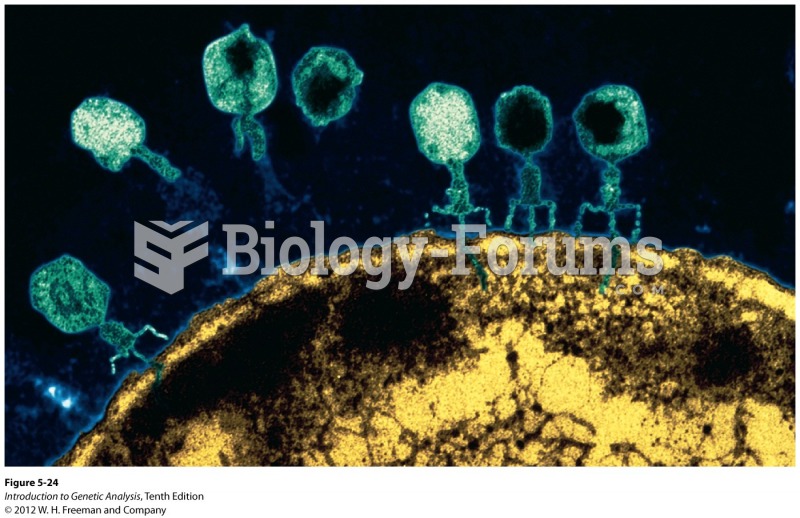
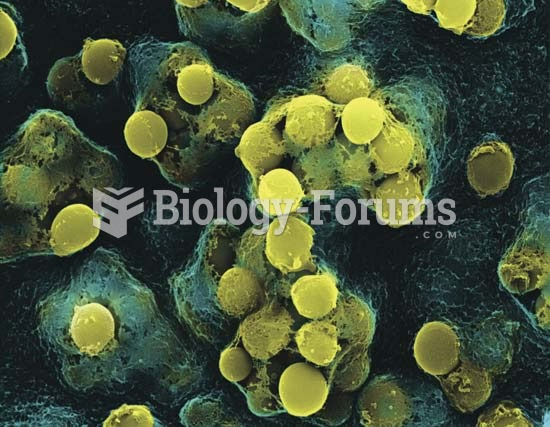
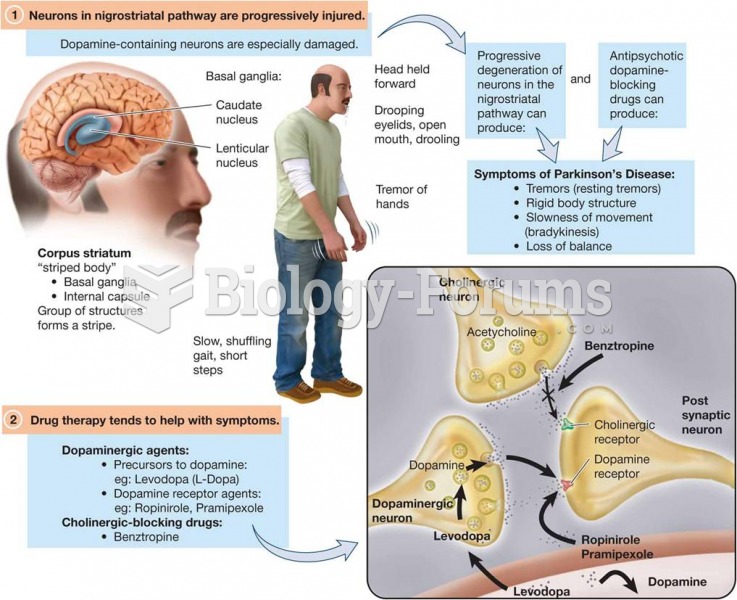
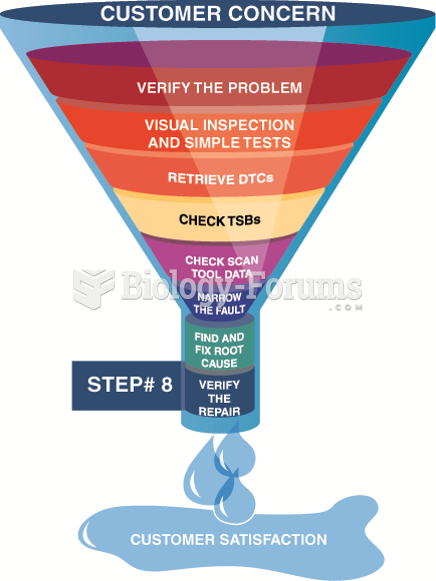
|
|
|
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.
After a vasectomy, it takes about 12 ejaculations to clear out sperm that were already beyond the blocked area.
The horizontal fraction bar was introduced by the Arabs.
There can actually be a 25-hour time difference between certain locations in the world. The International Date Line passes between the islands of Samoa and American Samoa. It is not a straight line, but "zig-zags" around various island chains. Therefore, Samoa and nearby islands have one date, while American Samoa and nearby islands are one day behind. Daylight saving time is used in some islands, but not in others—further shifting the hours out of sync with natural time.
Bacteria have been found alive in a lake buried one half mile under ice in Antarctica.