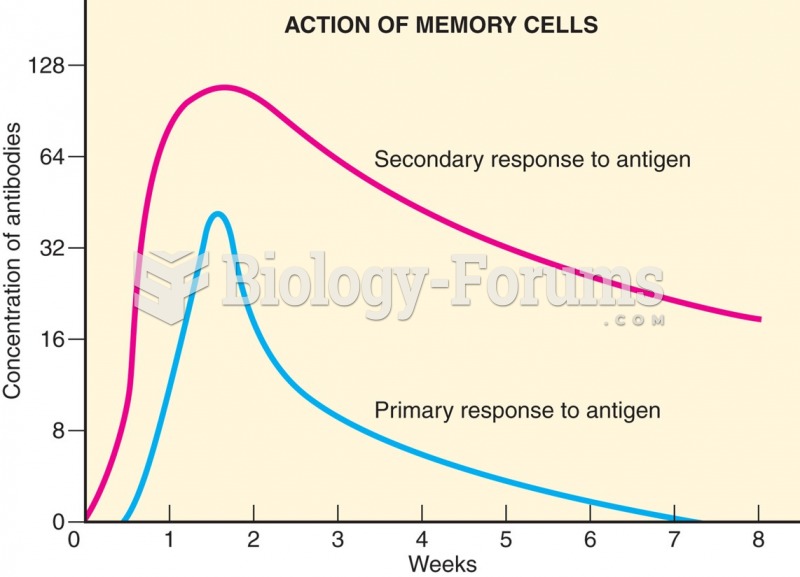
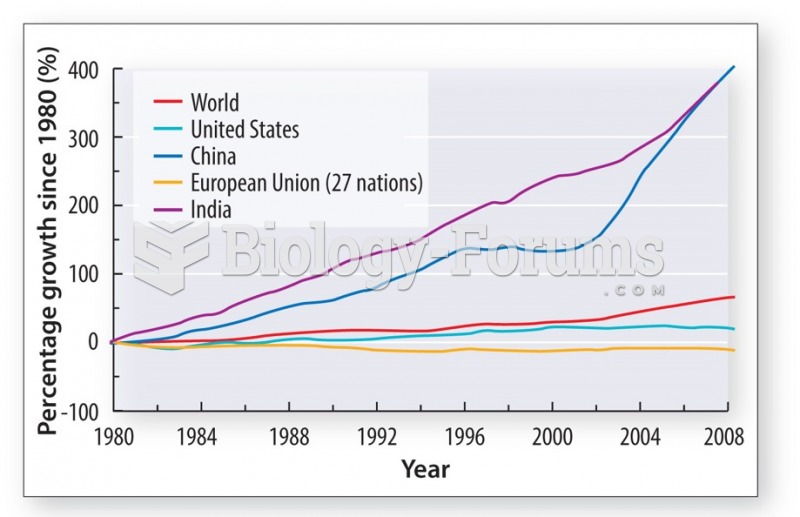
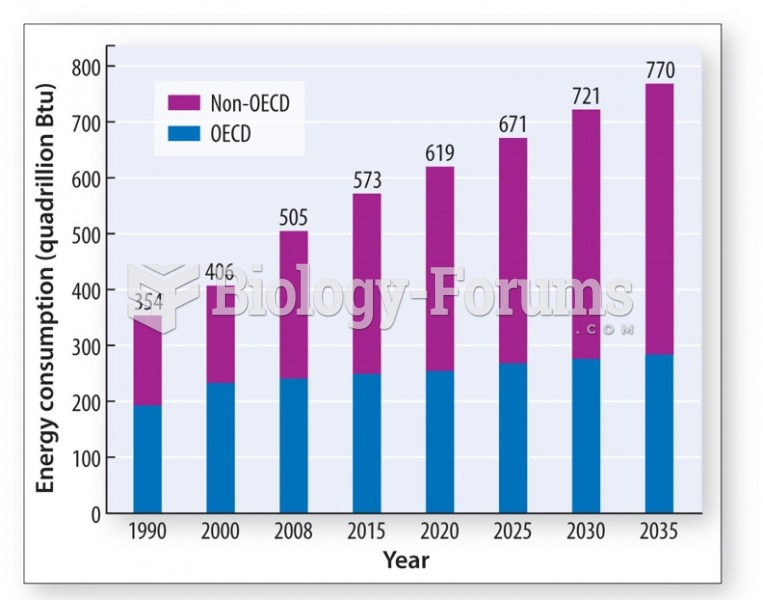
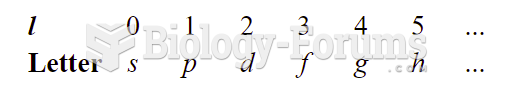|
|
|
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
The training of an anesthesiologist typically requires four years of college, 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of residency.
Cyanide works by making the human body unable to use oxygen.
Most women experience menopause in their 50s. However, in 1994, an Italian woman gave birth to a baby boy when she was 61 years old.