This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
More than 150,000 Americans killed by cardiovascular disease are younger than the age of 65 years.
Did you know?
There are actually 60 minerals, 16 vitamins, 12 essential amino acids, and three essential fatty acids that your body needs every day.
Did you know?
Patients who cannot swallow may receive nutrition via a parenteral route—usually, a catheter is inserted through the chest into a large vein going into the heart.
Did you know?
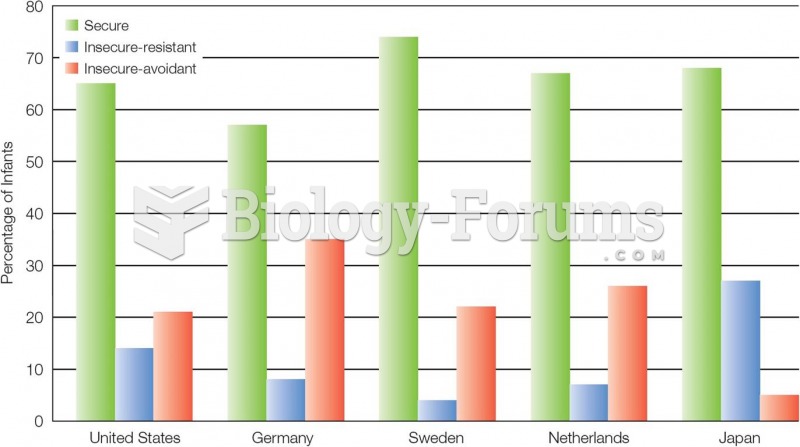
The people with the highest levels of LDL are Mexican American males and non-Hispanic black females.
Did you know?
To prove that stomach ulcers were caused by bacteria and not by stress, a researcher consumed an entire laboratory beaker full of bacterial culture. After this, he did indeed develop stomach ulcers, and won the Nobel Prize for his discovery.