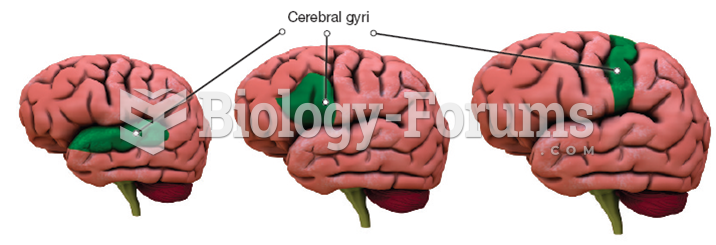
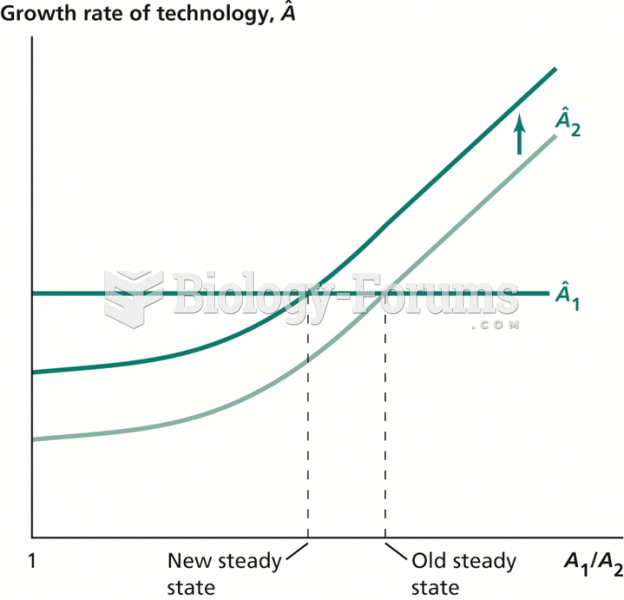
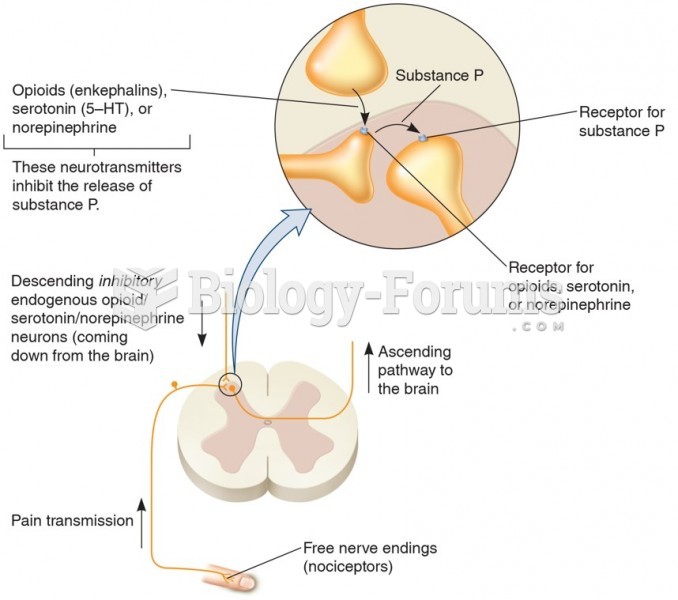
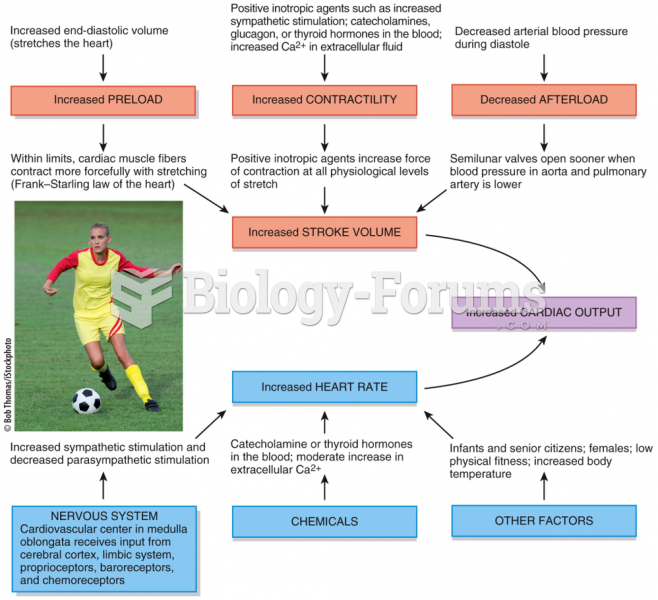
|
|
|
Chronic marijuana use can damage the white blood cells and reduce the immune system's ability to respond to disease by as much as 40%. Without a strong immune system, the body is vulnerable to all kinds of degenerative and infectious diseases.
In 2010, opiate painkllers, such as morphine, OxyContin®, and Vicodin®, were tied to almost 60% of drug overdose deaths.
To combat osteoporosis, changes in lifestyle and diet are recommended. At-risk patients should include 1,200 to 1,500 mg of calcium daily either via dietary means or with supplements.
Eating carrots will improve your eyesight. Carrots are high in vitamin A (retinol), which is essential for good vision. It can also be found in milk, cheese, egg yolks, and liver.
A recent study has found that following a diet rich in berries may slow down the aging process of the brain. This diet apparently helps to keep dopamine levels much higher than are seen in normal individuals who do not eat berries as a regular part of their diet as they enter their later years.