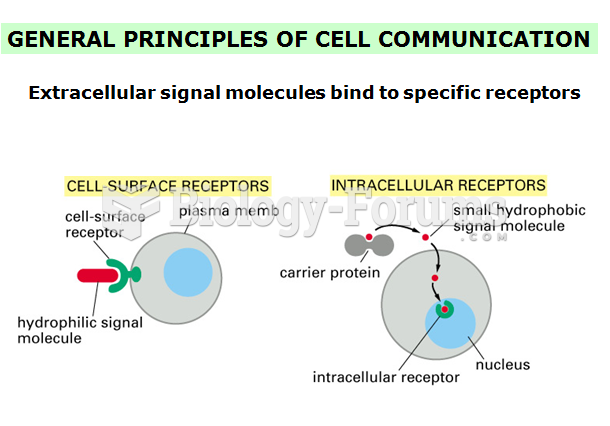
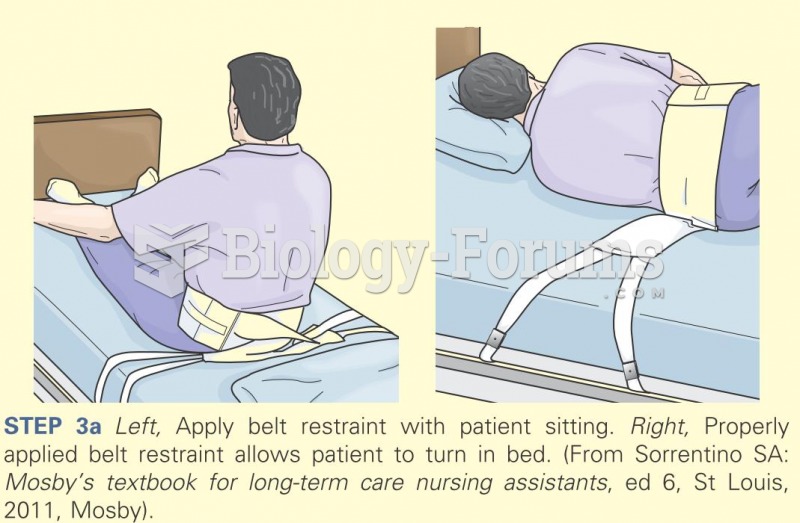
Answer to Question 1
Reliability is defined as the similarity between two rankings of test scores obtained from the same individual. The more test scores are free of measurement error, the greater the probability that two scores from the same individual will be the same. Validity is defined as how well a test measures what it claims to measure. Reliability and validity are both critical issues in testing. In order to make meaningful interpretations of students' test scores, tests must yield consistent scores and be measuring what the user intends to measure.
Three types of reliability were discussed in the text.
Test-retest reliability: This pertains to the stability of an individual's test score when given the same test on two separate occasions. If a test does not have test-retest reliability a student may score very well on one occasion and very poorly on a second occasion. This would make it impossible to finally determine an accurate indication of the individual's level of the characteristic being measured.
Alternate-form reliability: This pertains to the equivalence of two forms of a single test. Both forms should measure the same content using items of similar difficulty. If a test does not have this characteristic student performance would be affected by the form of the test they took when they should be able to take either form and score the same.
Split-half reliability: This pertains to the homogeneity or internal consistency of a test's items. They should all be working together to measure the same characteristic. If a test does not have this quality, some of its items will be measuring the intended characteristic while others will be measuring something else. For example, math word problems should not have difficult vocabulary. This would result in items measuring language skills rather than math skills.
Tests must be reliable in order for them to be valid. If a test's scores are not consistent over time, or forms of a test are not equivalent, or its items measure the wrong characteristics, appropriate conclusions regarding student performance cannot be made. However, when a test is valid, meaning that it is measuring the right thing and appropriate conclusions regarding student performance can be made, then we know it must be reliable.
Answer to Question 2
D