Answer to Question 1
C
Answer to Question 2
1.
Beginning Inventory + 2014 Production = 2014 Sales + Ending Inventory
85,000 units + 2014 Production = 345,400 units + 34,500 units
2014 Production = 294,900 units
Income Statement for the Zwatch Company, Variable Costing
for the Year Ended December 31, 2014
Revenues: 22 345,400 7,598,800
Variable costs
Beginning inventory: 5.10 85,000 433,500
Variable manufacturing costs: 5.10 294,900 1,503,990
Cost of goods available for sale 1,937,490
Deduct ending inventory: 5.10 34,500 (175,950)
Variable cost of goods sold 1,761,540
Variable operating costs: 1.10 345,400 379,940
Adjustment for variances 0
Total variable costs 2,141,480
Contribution margin 5,457,320
Fixed costs
Fixed manufacturing overhead costs 1,440,000
Fixed operating costs 1,080,000
Total fixed costs 2,520,000
Operating income 2,937,320
Absorption Costing Data
Fixed manufacturing overhead allocation rate =
Fixed manufacturing overhead/Denominator level machine-hours = 1,440,000 6,000
= 240 per machine-hour
Fixed manufacturing overhead allocation rate per unit =
Fixed manufacturing overhead allocation rate/standard production rate = 240 50
= 4.80 per unit
Income Statement for the Zwatch Company, Absorption Costing
for the Year Ended December 31, 2014
Revenues: 22 345,400 7,598,800
Cost of goods sold
Beginning inventory (5.10 + 4.80) 85,000 841,500
Variable manuf. costs: 5.10 294,900 1,503,990
Allocated fixed manuf. costs: 4.80 294,900 1,415,520
Cost of goods available for sale 3,761,010
Deduct ending inventory: (5.10 + 4.80) 34,500 (341,550)
Adjust for manuf. variances (4.80 5,100)a 24,480 U
Cost of goods sold 3,443,940
Gross margin 4,154,860
Operating costs
Variable operating costs: 1.10 345,400 379,940
Fixed operating costs 1,080,000
Total operating costs 1,459,940
Operating income 2,694,920
a Production volume variance = (6,000 hours 50) 294,900 4.80
= (300,000 294,900) 4.80
= 24,480
2. Zwatch's operating margins as a percentage of revenues are
Under variable costing:
Revenues 7,598,800
Operating income 2,937,320
Operating income as percentage of revenues 38.7
Under absorption costing:
Revenues 7,598,800
Operating income 2,694,920
Operating income as percentage of revenues 35.5
3. Operating income using variable costing is about 9 percent higher than operating income calculated using absorption costing.
Variable costing operating income Absorption costing operating income =
2,937,320 2,694,920 = 242,400
Fixed manufacturing costs in beginning inventory under absorption costing
Fixed manufacturing costs in ending inventory under absorption costing
= (4.80 85,000) (4.80 34,500) = 242,400
4. The factors the CFO should consider include
(a) Effect on managerial behavior.
(b) Effect on external users of financial statements.
I would recommend absorption costing because it considers all the manufacturing resources (whether variable or fixed) used to produce units of output. Absorption costing has many critics. However, the dysfunctional aspects associated with absorption costing can be reduced by
Careful budgeting and inventory planning.
Adding a capital charge to reduce the incentives to build up inventory.
Monitoring nonfinancial performance measures.
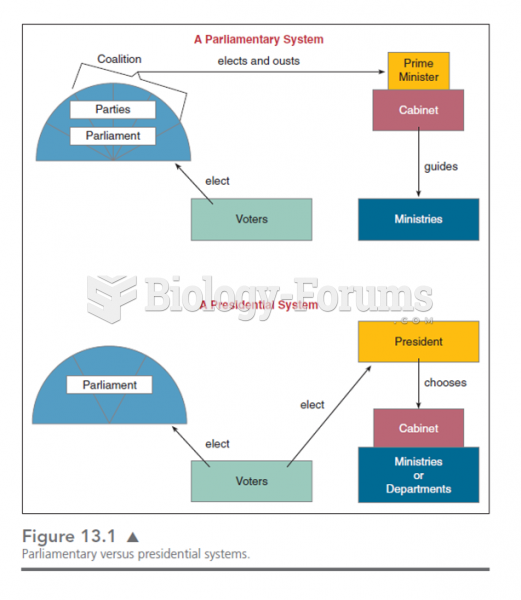 This chart shows the various lines of responsibility and how they differ in presidential and parliam
This chart shows the various lines of responsibility and how they differ in presidential and parliam
 Lewis Hine’s 1910 photograph shows a tenement alley in New York City. More famous for his “unsettlin
Lewis Hine’s 1910 photograph shows a tenement alley in New York City. More famous for his “unsettlin