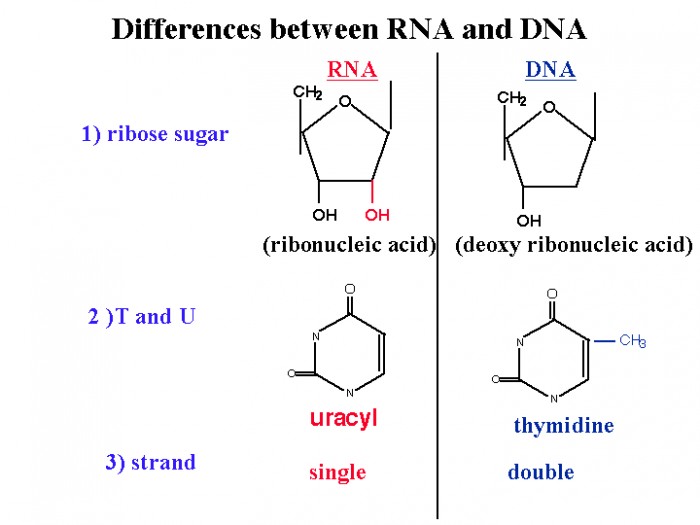
Answer to Question 1
Answer: China's political system is based on communism. Communism is set on the principle of community ownership. That is, all property, businesses, and natural resources are community owned, but these items are controlled by the single political party (Communist Party). Also, in communist societies, the government provides basic necessities based on need. In principle, citizens elect individuals to serve in the Communist Party, but that is rarely the case. In recent decades, China's economy has become more diverse. While maintaining communist control, economic growth has been fueled by market forces and capitalism. As a result, a growing segment of the population has gained considerable wealth and is adopting similar lifestyles as in the United States; that is, based on income and wealth. Still, one of the key challenges for the government has been to sustain adequate job growth for tens of millions of workers laid off from state-owned enterprises, migrants, and new entrants to the workforce. The U.S. economy is based on the idea of capitalism. Under capitalism, the government does not possess ownership of all land, businesses, or natural resources. This economic system relies on market forces in which supply and demand for products, services, and labor determine monetary value. For example, in Chapter 9, we discussed how supply and demand influences pay rates.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: Cultural values pertain to the norms for behaviors and beliefs. National culture is steeped in a country's history, and we can describe it based on a society's social traditions, political and economic philosophy, and legal system. Power distance describes the extent to which power is unequally distributed. High power distance cultures reinforce hierarchical control, and members generally do not expect justification for the actions taken by those in power. Low power distance cultures embrace greater equality and justification for actions, particularly where actions create a disadvantage to an individual or group. Germany is well known for a culture that rates low in power distance, whereas the United Arab Emirates is culture that strongly captures a high power distance orientation. Individualism refers to the extent to which an individual focuses on his or her own welfare relative to others. Collectivism describes a concern for the welfare of the larger group such as family, coworkers, or other groups. The United States and Canada are highly individualistic cultures, whereas Chile, China, and Mexico value collectivistic norms. Masculine cultures place high value on achievement, material award, and assertiveness. Feminine cultures espouse cooperation, modesty, and quality of life. Japan is an example of a highly masculine culture, whereas Norway and Finland embody the values of a feminine culture.