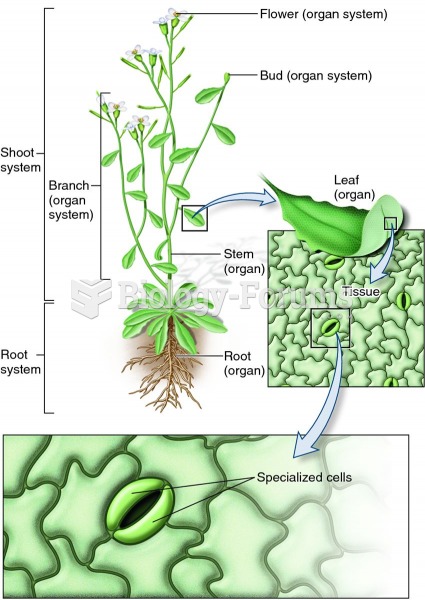
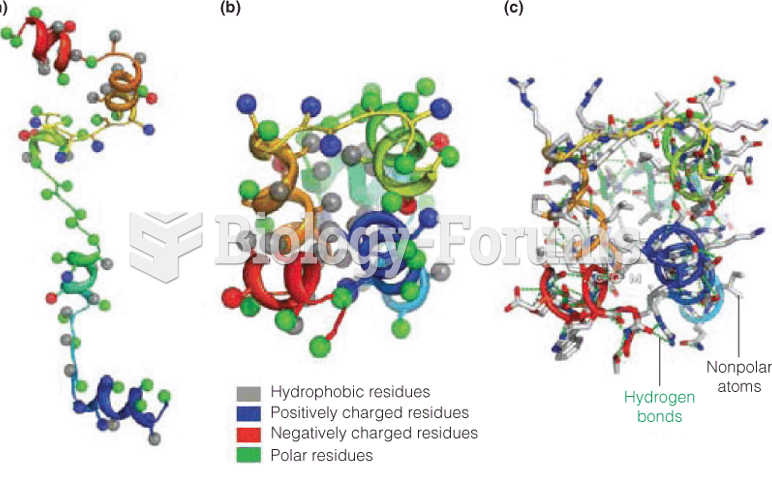
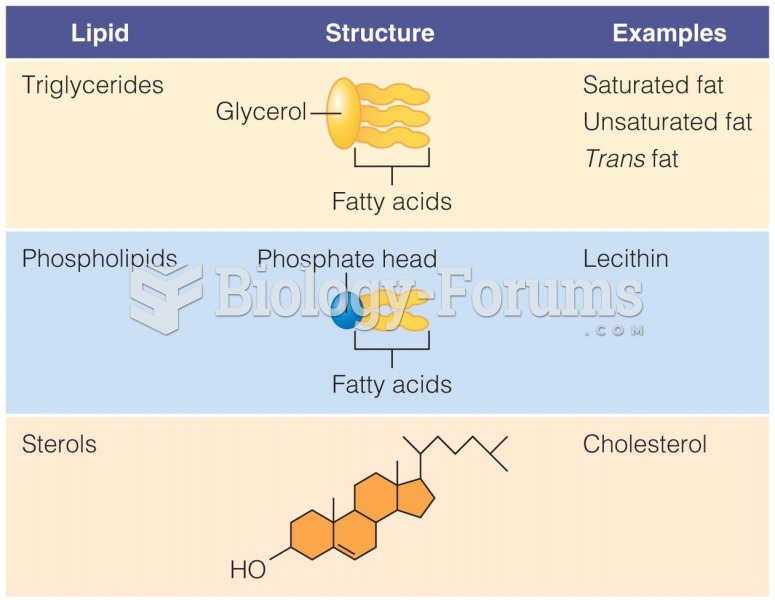
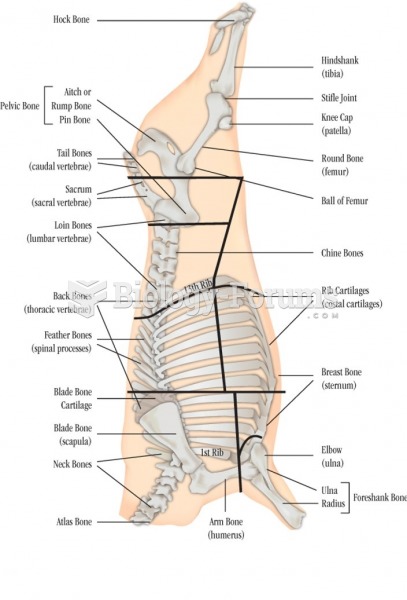
Answer to Question 1
Answer: D
Answer to Question 2
Answer: The mechanistic organization (or bureaucracy) was the natural result of combining work specialization, departmentalization, chain of command, span of control, centralization and decentralization, and formalization. Adhering to the chain-of-command principle ensured the existence of a formal hierarchy of authority, with each person controlled and supervised by one superior. Keeping the span of control small at increasingly higher levels in the organization created tall, impersonal structures. As the distance between the top and the bottom of the organization expanded, top management would increasingly impose rules and regulations.
Because top managers could not control lower-level activities through direct observation and ensure the use of standard practices, they substituted rules and regulations. The belief in a high degree of work specialization created jobs that were simple, routine, and standardized. Further specialization through the use of departmentalization increased impersonality and the need for multiple layers of management to coordinate the specialized departments. This created a mechanistic organization with high specialization, rigid departmentalization, a clear chain of command, narrow spans of control, centralization, and high formalization
The organic organization is a highly adaptive form that is as loose and flexible as the mechanistic organization is rigid and stable. The organic organization's loose structure allows it to change rapidly as required. It has division of labor, but the jobs people do are not standardized. Employees tend to be professionals who are technically proficient and trained to handle diverse problems. They need few formal rules and little direct supervision because their training has instilled in them standards of professional conduct. Thus, an organic organization has cross-functional teams, cross-hierarchical teams, free flow of information, wide spans of control, decentralization, and low formalization.