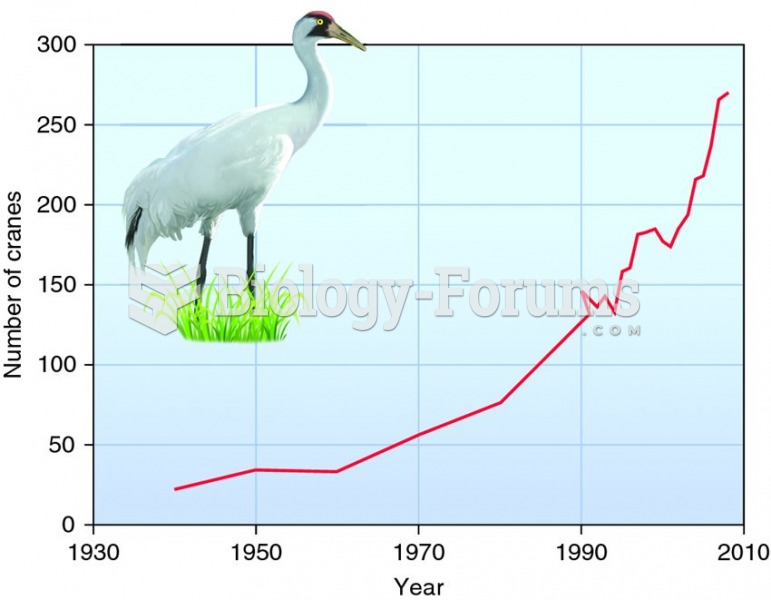
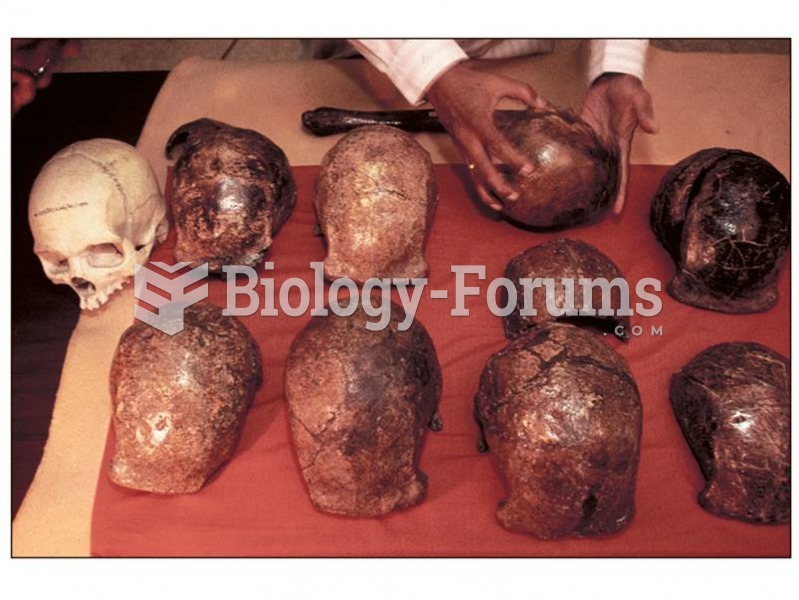
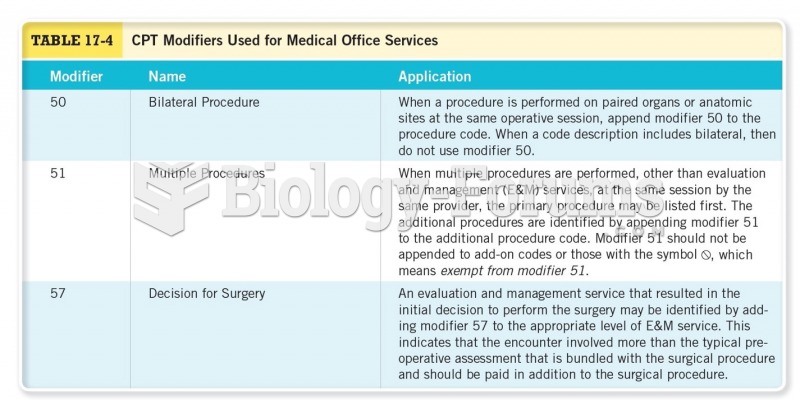
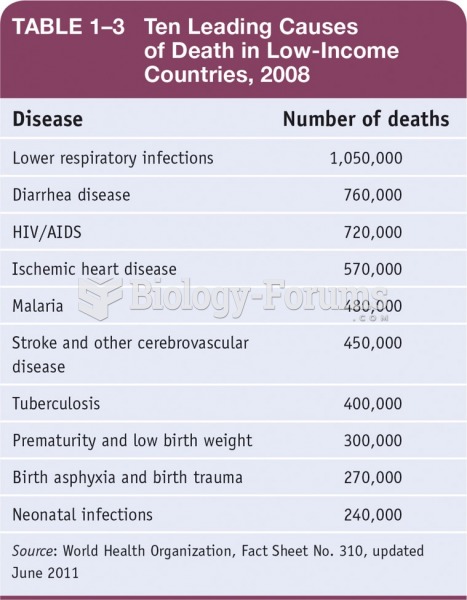
Tim Wrench was leading the client services division of AmWeb for seven years when he was asked to move to another region where the company was setting up its office. Before moving, Tim was asked to help in finding a successor for him from his team.
Tim's most obvious choice was Judy Judge, and the management accepted his choice as Judy was a popular person across the company. Judy was known for her vivacious nature, was often seen speaking to employees from various divisions, and was always excited to take up a new opportunity. Once she became a leader, she continued to give employees freedom and flexibility even if it resulted in deficiencies on the work front like missed deadlines or low quality. Judy's initial weeks as a leader were full of confusion among her team members, but many felt that the situation would come under control. When things did not improve in the next two months and many complaints poured in from clients, the management realized that Judy was not the best candidate to lead the team. Which of the following, if true, would best explain this outcome?
A) Judy was a high-performing employee and enjoyed good relationships with everyone on the team.
B) Everyone felt Judy was given insufficient time to prove her worth as a leader.
C) Research has shown that traits can predict the emergence of a leader, but not his or her efficiency as a leader.
D) The client complaints were a common thing encountered by the company.
E) Judy demonstrated low levels of consideration and high levels of task-orientation.
Question 2
A research group in Arizona recently conducted a survey among workers of a coal power plant to understand emotions and their happiness quotient. Employees at the plant often complained about poor working conditions and low insurance benefits.
However, the group was surprised with the findings of the survey because employees had a positive mood 70 percent of the time during work hours. Which of the following concepts would best explain such findings?
A) butterfly effect
B) framing effect
C) anchoring bias
D) distinction bias
E) positivity offset