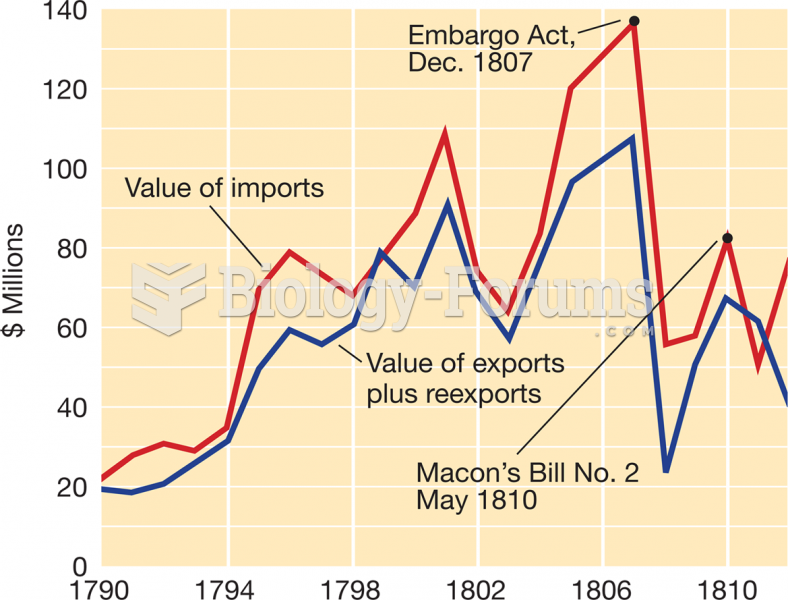
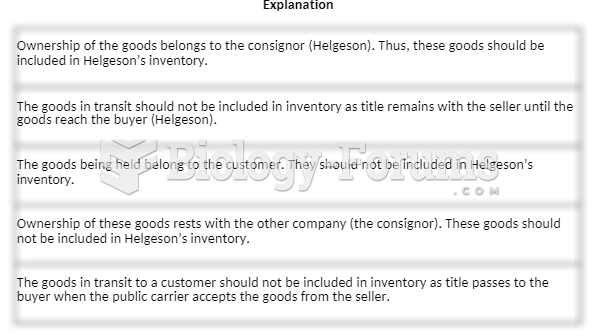
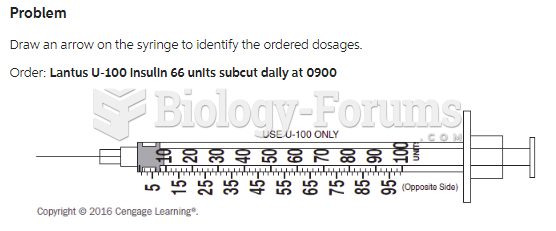
Answer to Question 1
C
Answer to Question 2
1. Subsidies-Financial assistance to domestic producers in the form of cash payments, low-interest loans, tax breaks, product price supports, or other forms is called a subsidy. Regardless of the form a subsidy takes, it is intended to assist domestic companies in fending off international competitors. This can mean becoming more competitive in the home market or increasing competitiveness in international markets through exports.
2. Export Financing-Governments often promote exports by helping companies finance their export activities. They can offer loans that a company could otherwise not obtain or charge them an interest rate that is lower than the market rate. Another option is for a government to guarantee that it will repay the loan of a company if the company should default on repayment; this is called a loan guarantee.
3. Foreign Trade Zones-Most countries promote trade with other nations by creating what is called a foreign trade zone (FTZ)a designated geographic region through which merchandise is allowed to pass with lower customs duties (taxes) and/or fewer customs procedures. Increased employment is often the intended purpose of foreign trade zones, with a by-product being increased trade.
4. Special Government Agencies-The governments of most nations have special agencies responsible for promoting exports. Such agencies can be particularly helpful to small and medium-sized businesses that have limited financial resources. Government trade promotion agencies often organize trips for trade officials and businesspeople to visit other countries to meet potential business partners and generate contacts for new business. They also typically open trade offices in other countries. These offices are designed to promote the home country's exports and introduce businesses to potential partners in the host nation. Government trade promotion agencies typically do a great deal of advertising in other countries to promote the nation's exports.