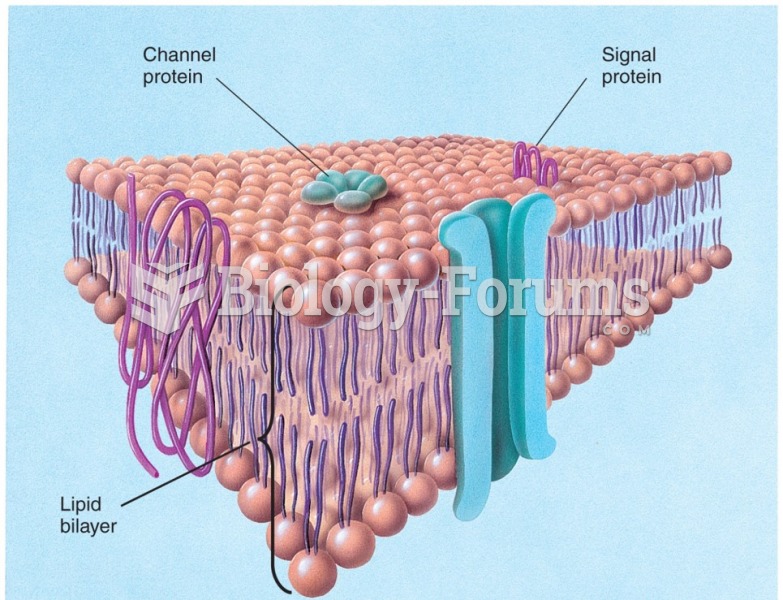
Answer to Question 1
B
Answer to Question 2
Formed in 1969, the Andean Community includes four South American countries located in the Andes mountain rangeBolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. Today the Andean Community comprises a market of around 97 million consumers and a combined GDP of about 220 billion. The main objectives of the group include tariff reduction for trade among member nations, a common external tariff, and common policies in both transportation and certain industries. The Andean Community had the ambitious goal of establishing a common market by 1995, but delays mean that it remains a somewhat incomplete customs union.
Several factors hamper progress. Political ideology among member nations is somewhat hostile to the concept of free markets and favors a good deal of government involvement in business affairs. Also, inherent distrust among members makes lower tariffs and more open trade hard to achieve. The common market will be difficult to implement within the framework of the Andean Community. One reason is that each country has been given significant exceptions in the tariff structure that they have in place for trade with nonmember nations. Another reason is that countries continue to sign agreements with just one or two countries outside the Andean Community framework. Independent actions impair progress internally and hurt the credibility of the Andean Community with the rest of the world.
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) was formed in 1975 but restarted efforts at economic integration in 1992 because of a lack of early progress. One of the most important goals of ECOWAS is the formation of a customs union, an eventual common market, and a monetary union. Together, the ECOWAS nations comprise a large portion of the economic activity in sub-Saharan Africa.
Progress on market integration is almost nonexistent. In fact, the value of trade occurring among ECOWAS nations is just 11 percent of the value that the trade members undertake with third parties. But ECOWAS has made progress in the free movement of people, construction of international roads, and development of international telecommunication links. Some of its main problems are due to political instability, poor governance, weak national economies, poor infrastructures, and poor economic policies.