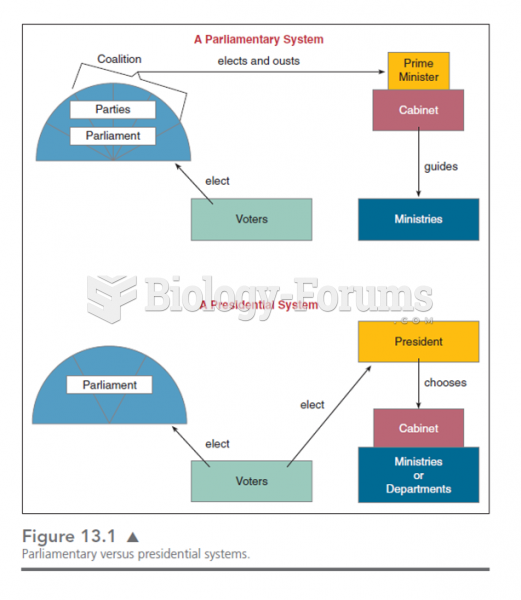
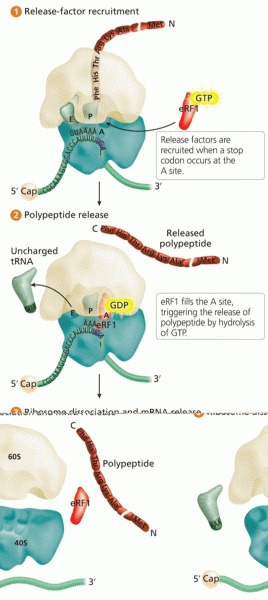
|
|
|
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.
Excessive alcohol use costs the country approximately $235 billion every year.
When Gabriel Fahrenheit invented the first mercury thermometer, he called "zero degrees" the lowest temperature he was able to attain with a mixture of ice and salt. For the upper point of his scale, he used 96°, which he measured as normal human body temperature (we know it to be 98.6° today because of more accurate thermometers).
Allergies play a major part in the health of children. The most prevalent childhood allergies are milk, egg, soy, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood.
Though newer “smart” infusion pumps are increasingly becoming more sophisticated, they cannot prevent all programming and administration errors. Health care professionals that use smart infusion pumps must still practice the rights of medication administration and have other professionals double-check all high-risk infusions.
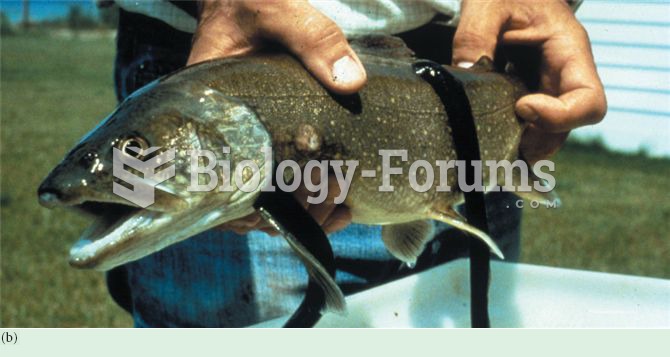 Invasive species in Canada include (a) zebra mussels, Dreissena polymorpha, (b) sea lamprey, Petromy
Invasive species in Canada include (a) zebra mussels, Dreissena polymorpha, (b) sea lamprey, Petromy
 Invasive species in Canada include (a) zebra mussels, Dreissena polymorpha, (b) sea lamprey, Petromy
Invasive species in Canada include (a) zebra mussels, Dreissena polymorpha, (b) sea lamprey, Petromy