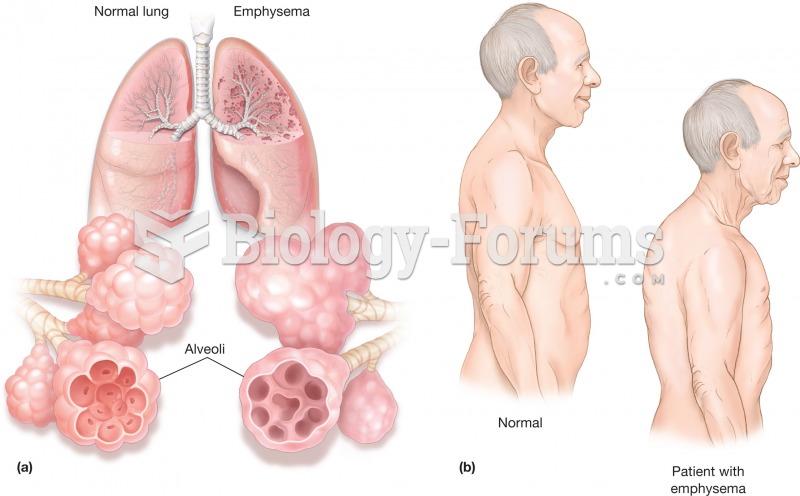
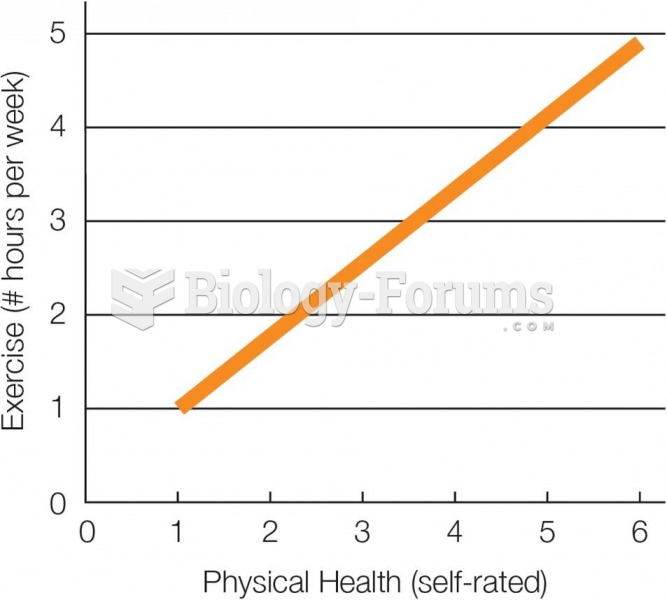
|
|
|
Patients who have undergone chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer often complain of a lack of mental focus; memory loss; and a general diminution in abilities such as multitasking, attention span, and general mental agility.
The average person is easily confused by the terms pharmaceutics and pharmacology, thinking they are one and the same. Whereas pharmaceutics is the science of preparing and dispensing drugs (otherwise known as the science of pharmacy), pharmacology is the study of medications.
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
If you use artificial sweeteners, such as cyclamates, your eyes may be more sensitive to light. Other factors that will make your eyes more sensitive to light include use of antibiotics, oral contraceptives, hypertension medications, diuretics, and antidiabetic medications.
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
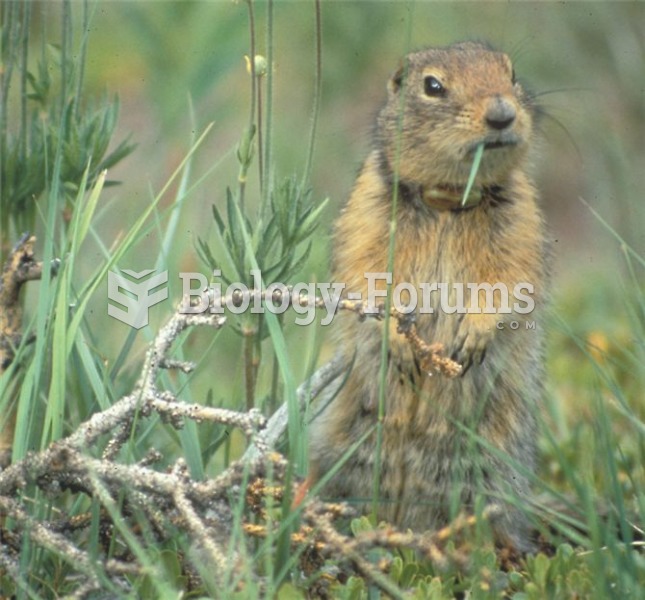 Organisms exhibit a diversity of behaviours, which include (clockwise from upper left), foraging and
Organisms exhibit a diversity of behaviours, which include (clockwise from upper left), foraging and
 Invasive species in Canada include (a) zebra mussels, Dreissena polymorpha, (b) sea lamprey, Petromy
Invasive species in Canada include (a) zebra mussels, Dreissena polymorpha, (b) sea lamprey, Petromy