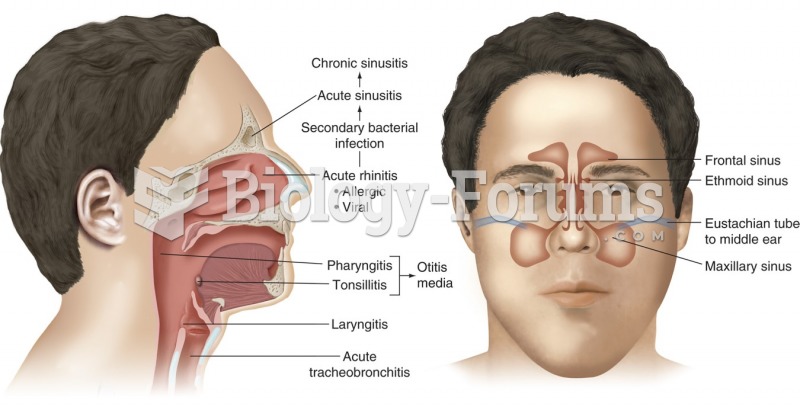
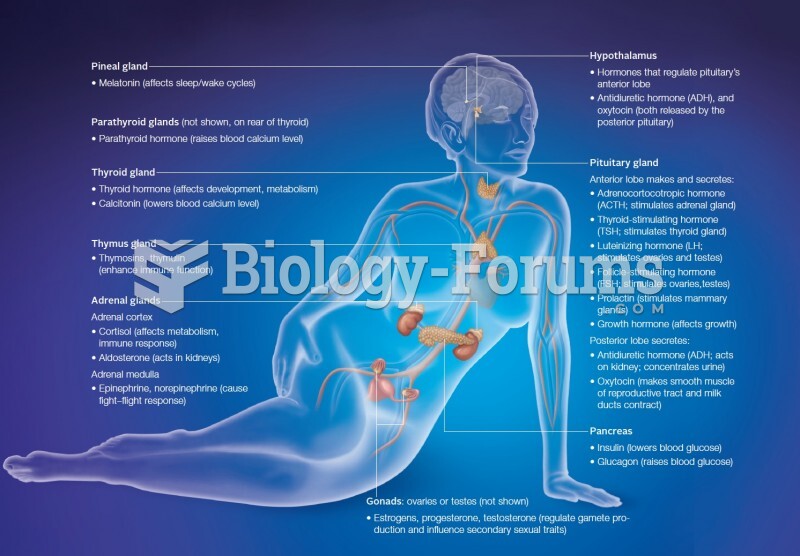
|
|
|
The types of cancer that alpha interferons are used to treat include hairy cell leukemia, melanoma, follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma.
Certain topical medications such as clotrimazole and betamethasone are not approved for use in children younger than 12 years of age. They must be used very cautiously, as directed by a doctor, to treat any child. Children have a much greater response to topical steroid medications.
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
Approximately 25% of all reported medication errors result from some kind of name confusion.
Patients should never assume they are being given the appropriate drugs. They should make sure they know which drugs are being prescribed, and always double-check that the drugs received match the prescription.