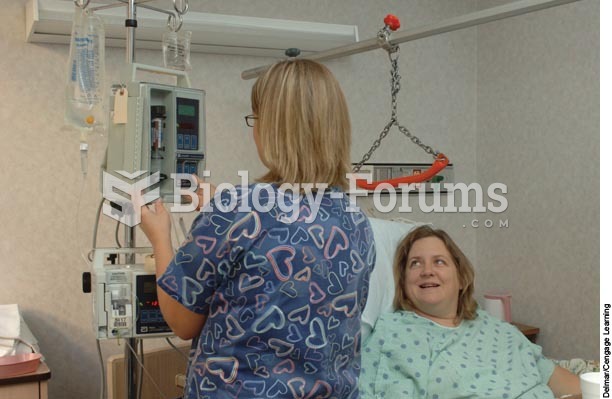|
|
|
There are more bacteria in your mouth than there are people in the world.
Sperm cells are so tiny that 400 to 500 million (400,000,000–500,000,000) of them fit onto 1 tsp.
Though newer “smart” infusion pumps are increasingly becoming more sophisticated, they cannot prevent all programming and administration errors. Health care professionals that use smart infusion pumps must still practice the rights of medication administration and have other professionals double-check all high-risk infusions.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%.
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.