|
|
|
Although puberty usually occurs in the early teenage years, the world's youngest parents were two Chinese children who had their first baby when they were 8 and 9 years of age.
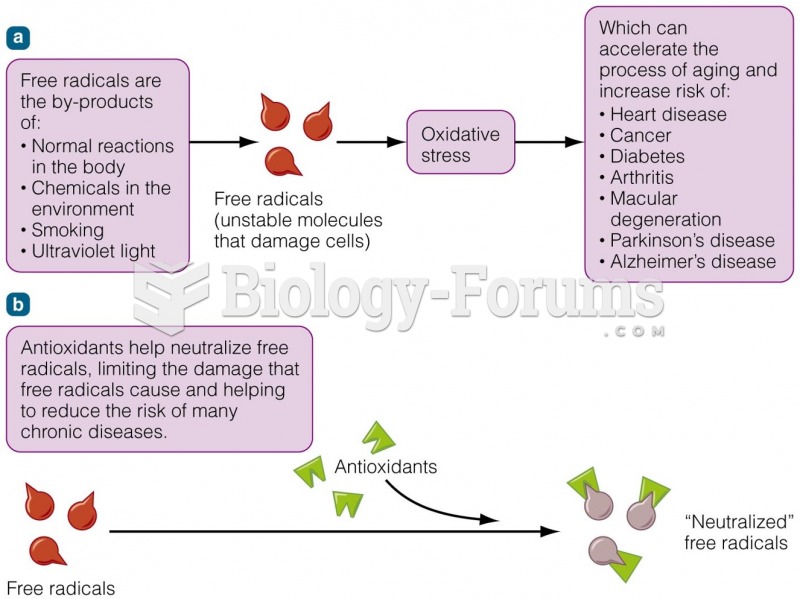
Alzheimer's disease affects only about 10% of people older than 65 years of age. Most forms of decreased mental function and dementia are caused by disuse (letting the mind get lazy).
There can actually be a 25-hour time difference between certain locations in the world. The International Date Line passes between the islands of Samoa and American Samoa. It is not a straight line, but "zig-zags" around various island chains. Therefore, Samoa and nearby islands have one date, while American Samoa and nearby islands are one day behind. Daylight saving time is used in some islands, but not in others—further shifting the hours out of sync with natural time.
More than 30% of American adults, and about 12% of children utilize health care approaches that were developed outside of conventional medicine.
Asthma cases in Americans are about 75% higher today than they were in 1980.
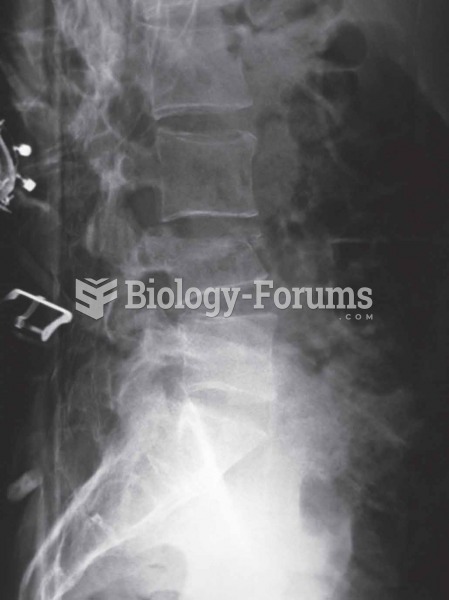 Vertebral compression Fractures of the spine (vertebra) can cause severe ”band-like” pain that radia
Vertebral compression Fractures of the spine (vertebra) can cause severe ”band-like” pain that radia
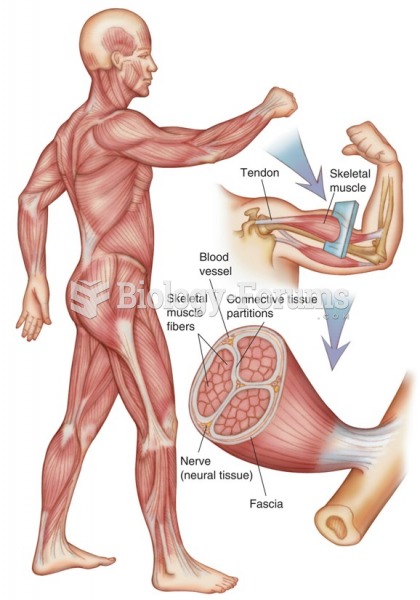 skeletal muscle consists of a group of fibers held together by connective tissue. It is enclosed in ...
skeletal muscle consists of a group of fibers held together by connective tissue. It is enclosed in ...