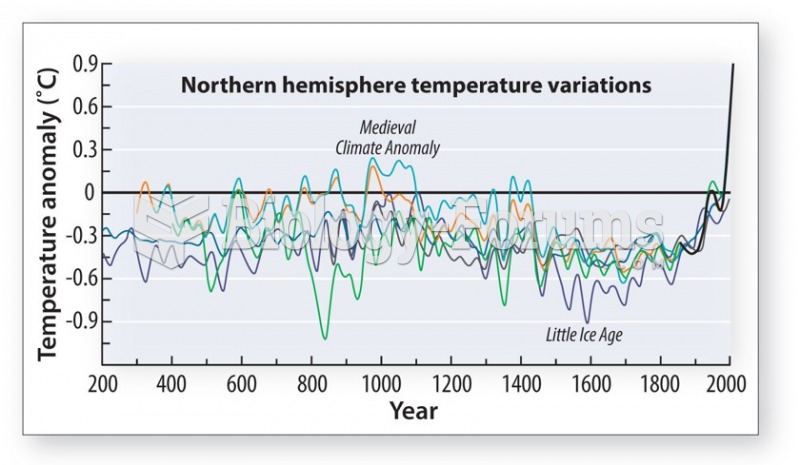
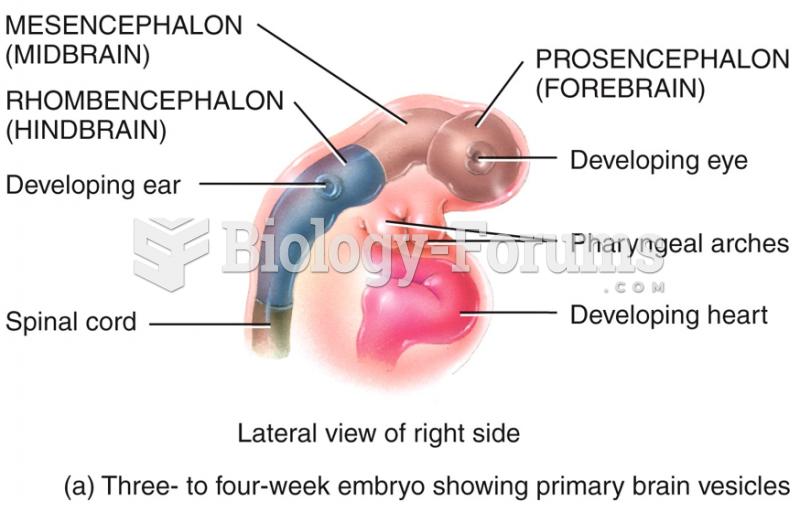
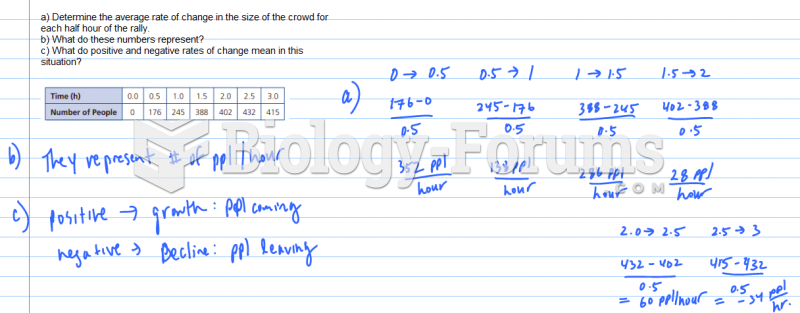
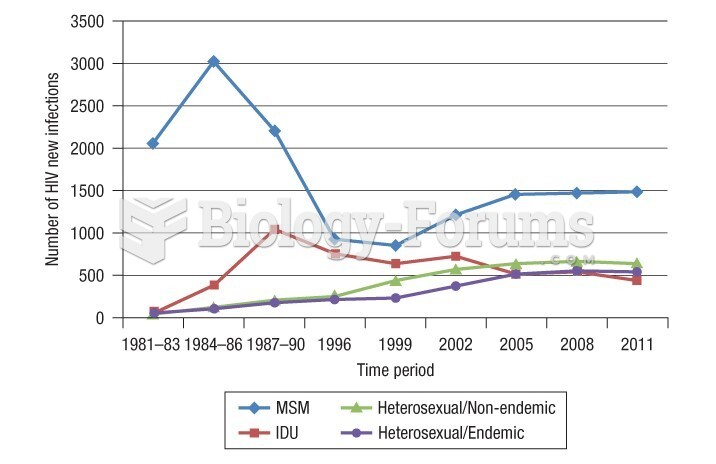
Answer to Question 1
An ideal response will:
1, Define realignment as a rare event in American politics often associated with a major national crisis. Critical elections, economic crisis, or war may be key precipitators.
2, Explain that major disagreements in policy result in a shift in coalition formation and subsequently, one party takes over power from another, often lasting for decades. For example, the Republican Party emerged strongly from the Civil War, and the New Deal coalition became dominant following the Great Depression.
Answer to Question 2
An ideal response will:
1, Define the parties at war era as the current party era that began in the mid-1990s with the historic victory for Republicans in the 1994 congressional elections, when they gained control of both houses of Congress for the first time since 1946, and the successful effort by House Republicans to impeach Democratic president Bill Clinton in 1998, although the vote to remove him from office fell short.
2, Explain that national elections since 2000 have been fought by two well-funded and ideologically unified parties with strategy that has increasingly focused on using emotional appeals to voters, and election outcomes (with the exception of 2006) in state and national races have been extremely close.
3, Note that in the governing process, bipartisanship has been largely absent; partisan views have become more extreme as moderates in the parties have become more rare, debates have been bitter and lacking in civility, agreements have been difficult to reach because compromise with the other party has been seen as traitorous, and the result has been a divided government and gridlock.
4, Propose that party polarization may be more of an elite affair than a reflection of American views, since the public at large has remained fairly moderate or middle-of-the-road on most of the issues that are dividing the parties.