Please use a better topic title next time

1) What is the most accurate description of the relative importance of hunting versus gathering in foraging societies in terms of nutrition? In terms of place in society?
Hunting and gathering have remained the most ancient of human subsistence patterns. They remained the subsistence pattern of some societies even in the 20th century. Foraging societies are generally found to be passively dependent on what the society contains. They do not plant crops and keep only dogs as pets. Hunting and gathering play an important role from various points of view in a foraging society apart from nutrition. In case of nutrition hunting and gathering are believed to play an equally important role in the foraging societies. However, hunting has been done generally by men in groups. The foragers have been hunting to meet their caloric needs and as such hunting has relatively higher importance because of the meat being high in protein. Moreover, people in the foraging societies used to eagerly look for large hunts and whenever one was killed it was distributed among all the camp members.
However, men generally focussed on getting large hunts and one was not available always. As such gathering was another important means to get food. With time hunting large animals became unreliable and in some societies the diet came from nonmeat sources like nuts and roots mainly. In such a case gathering was the main source of food and gathering took precedence over hunting. Men used to look for large hunt but most of the diet used to come from vegetable sources.
Apart from nutrition hunting and gathering were also important from the point of view of division of labor. Hunting was the task of men and women were gatherers mainly. As the dependency of the foraging societies on vegetable food increased the women’s responsibility also increased as they had to collect and provide for the majority of the calories being consumed. In such a case, hunting and gathering have also been important from the point of view of defining gender roles. Men generally have little to do with food and child keeping other than hunting occasionally.
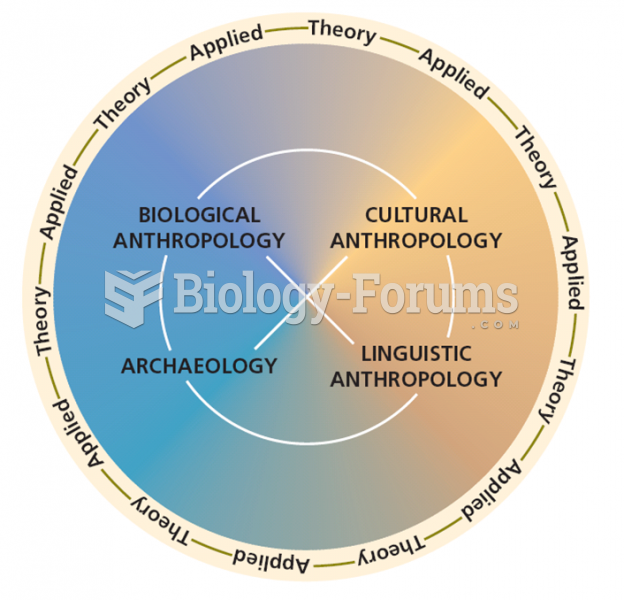
2) Larger societies include groups whose organization can be categorized as bands, tribes, chiefdoms, and states. What type of organizational structure would you argue that the Hutterites fall under? Please explain your reasoning.
The Hutterites had come to North America in the 1870s from Eastern Europe mainly to escape religious persecution. They are also the oldest continuous communal religious order in United States. They had originally settled in South Dakota in 1874 and their colonies are mainly in rural areas and are self-sustaining. They grow and raise enough to feed a colony of 60 to 10 residents. Every Hutterite colony has a corporate like structure with the minister or the Prediger as its Chief Executive. The minister takes the day to day decisions with support from advisory board. His duties also include managing the church affairs, marriages, funerals and managing the colony. The advisory board consists of members elected for life that include the minister, the colony manager, the farm manager and two to three witness brothers. These people together make all the important day to day decisions. As a whole this group is known as Zullbreider. The corporate like structure of the Hutterite colonies has also resulted in high efficiency in terms of farming and business operations.
In their organizational structure, the Hutterite colonies resemble the chiefdoms which are classless and have one or more permanent full time leaders. The minister and the advisory council members are permanent full time members. As in some chiefdoms, the Hutterite colonies also have an advisory council to assist the chief or the minister at making important decisions. The functions of the chief in a Hutterite colony is also similar to that of the chief in chiefdoms which is to oversee important matters and make key decisions apart from overseeing economic affairs and the distribution of production. Thus, it can be seen that the Hutterite colonies are the closest to the chiefdoms in their organizational structure.