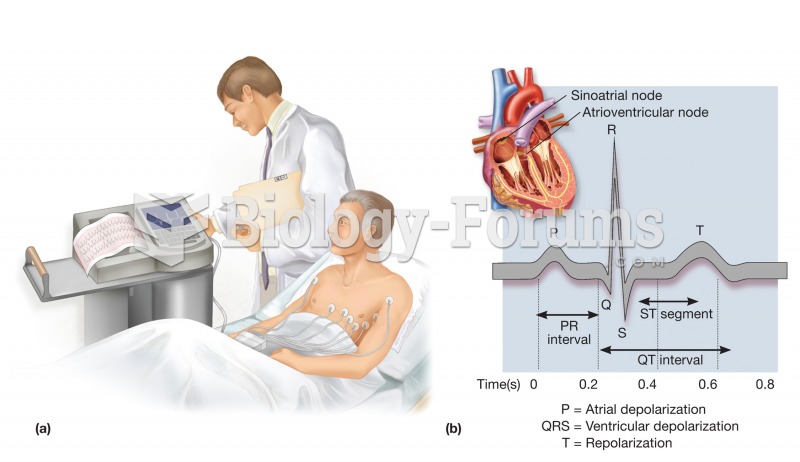
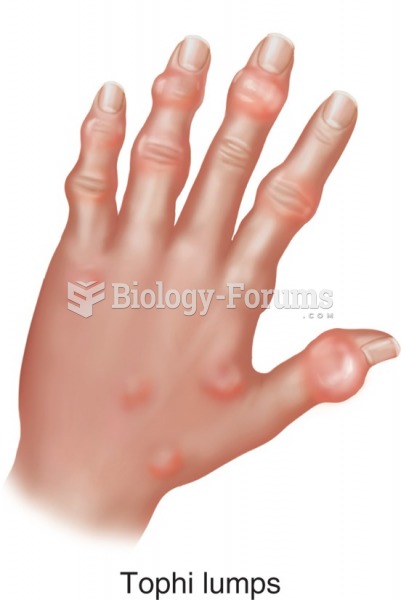
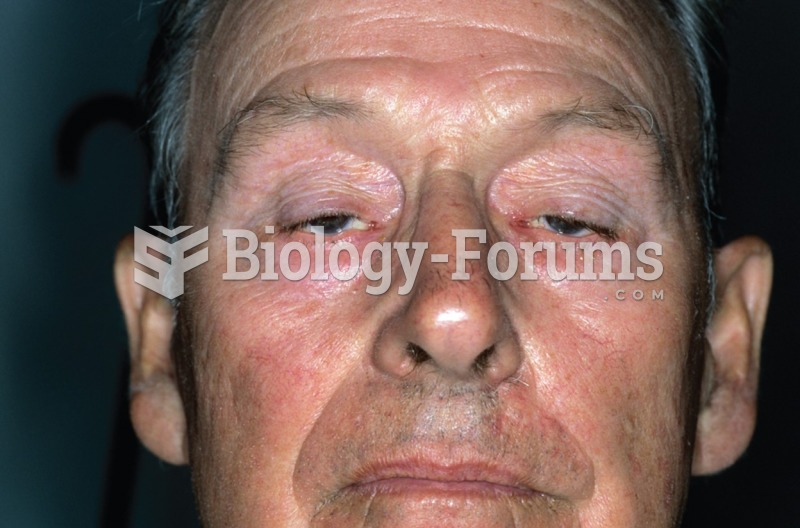
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen in water (H2O) is 2:1.
Did you know?
There are actually 60 minerals, 16 vitamins, 12 essential amino acids, and three essential fatty acids that your body needs every day.
Did you know?
In 2012, nearly 24 milliion Americans, aged 12 and older, had abused an illicit drug, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
Did you know?
Approximately 25% of all reported medication errors result from some kind of name confusion.
Did you know?
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).