Answer to Question 1
A, C, B, D
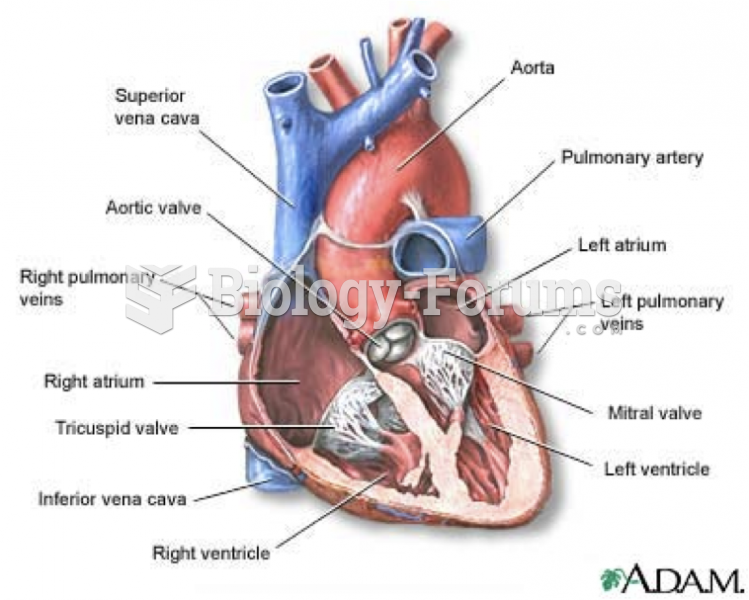
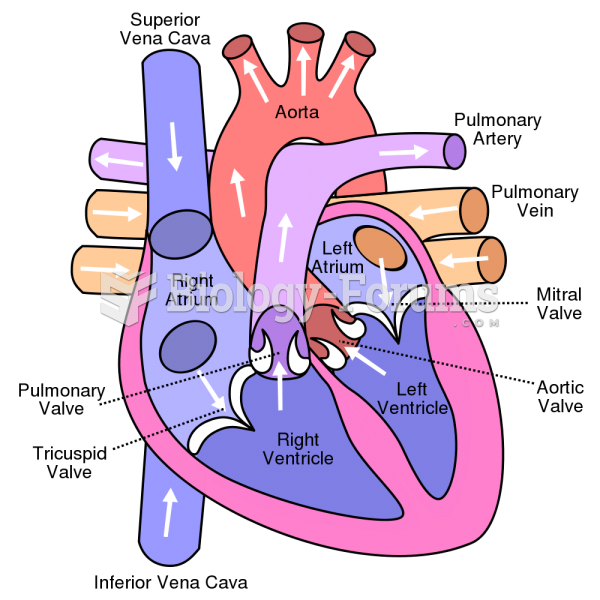
The nurse assesses the SaO2 because airway and breathing are the two most basic human needs on Maslow's Hierarchy of Human Needs. Assessing the SaO2 is also the first step for this indi-vidual because hypoxemia can explain the cool extremities and tachycardia with an adequate cardiac output. The nurse then examines the heart's rhythm; with adequate oxygenation, the cool extremities and increased heart rate can be explained by a low cardiac output as a result of dys-rhythmia; the heart becomes an ineffective pump when it beats too quickly, too slowly, or in an irregular pattern. Next, the nurse examines the blood pressure; hypotension as a result of low cardiac output and with adequate oxygen and a regular heart rhythm can explain the cool extrem-ities and tachycardia as the body tries to compensate by shunting blood to the vital organs and increasing the heart rate. Finally, the nurse examines the urine output to assess renal perfusion. With adequate oxygenation and a regular heart rhythm, urine output will drop with a low cardiac output because it decreases renal perfusion. The kidneys need a minimum systolic blood pressure of 80 mm Hg to produce urine.
Answer to Question 2
C
Feedback
A Incorrect. Sputum cultures are indicated to assess a resident for pneumonia; blood cultures are likely to show no growth unless the resident has severe sepsis.
B Incorrect. A chest x-ray study is a nonsensitive, nonspecific diagnostic tool for determining the presence of pneumonia in an older adult.
C Correct. Sputum is a sensitive and specific clinical indicator of pneumonia for older adults in nursing homes. If pneumonia is causing this resident's anorexia and tachycardia, the sputum should be cloudy, colored, and thick, especially if the resident is dehydrated, indicating an infection.
D Incorrect. Fever can be a late indicator of infection for an older adult.