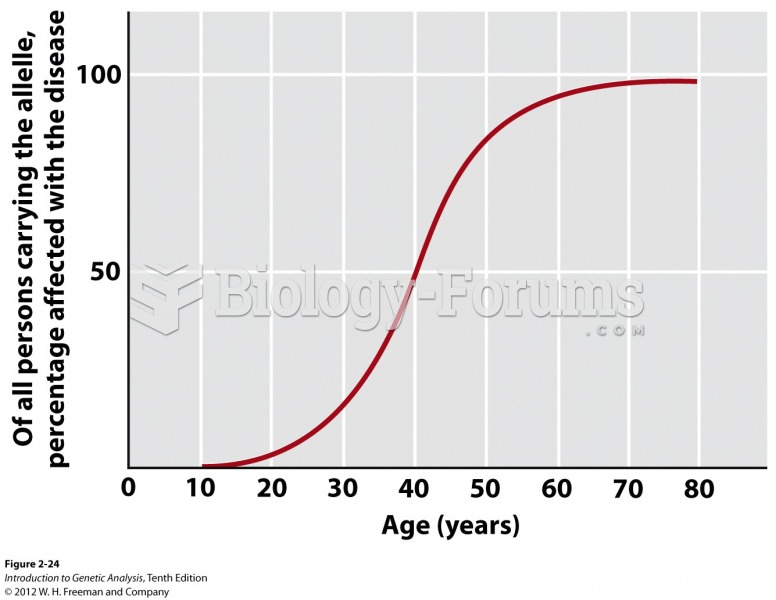
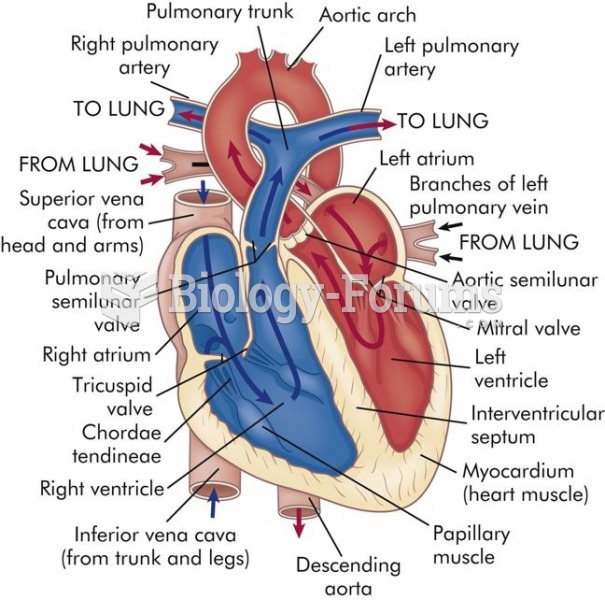
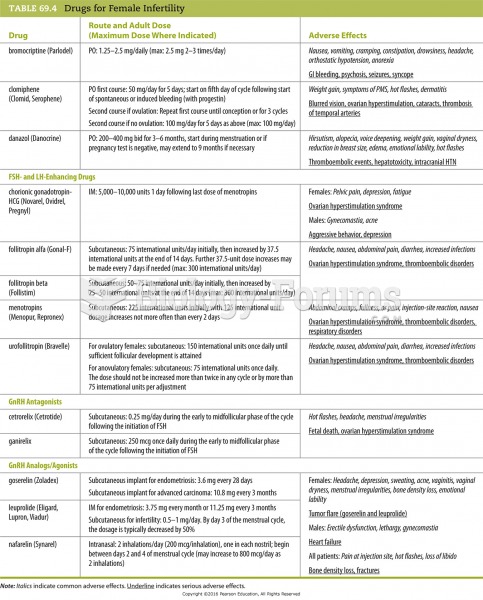
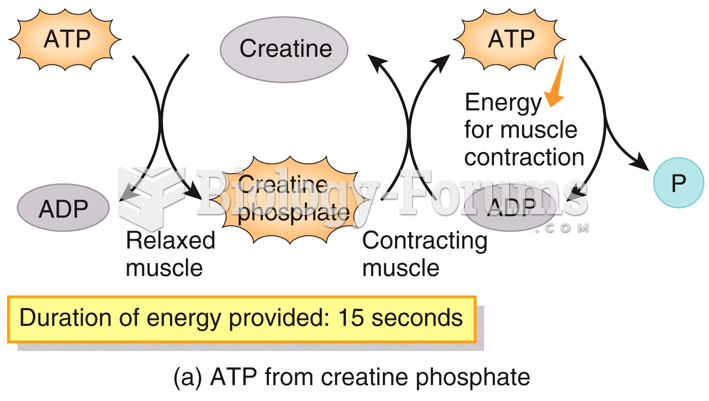
Answer to Question 1
D
Feedback
A Incorrect. A diuretic is a part of standard therapy for heart failure for controlling fluid balance but it does not interrupt neurohormonal activation from heart fail-ure.
B Incorrect. Nitroglycerin is common therapy for an ischemic myocardium to in-crease myocardial oxygenation, but it does not interrupt the neurohormonal ac-tivation from heart failure.
C Incorrect. Digoxin, a cardiac glycoside, is a part of standard heart failure therapy and acts as an inotropic agent to increase the force of myocardial contractions; however, it does not interrupt neurohormonal activation from heart failure.
D Correct. A beta-adrenergic blocker is an important part of standard therapy for patients with heart failure and is the drug of choice to break the neurohormonal cycle that aggravates heart failure. The beta blockers inhibit the action of epi-nephrine (epi) and norepinephrine (NE) to decrease myocardial workload and lower myocardial tissue oxygen demands. This woman's heart is an ineffective pump because it is ischemic, so it is unable to meet the body's metabolic de-mands. An ischemic heart has difficulty obtaining the supply of oxygen it needs to maintain cardiac output. As a result, the hypoxic myocardium stimulates the sympathetic nervous system to release epi and NE for shunting blood from the periphery to vital organs, the fight or flight mechanism. The release of epi and NE causes vasoconstriction and subsequent hypertension. These make the work of the heart more difficult because the heart must work harder to pump blood out of the left ventricle against a higher afterload. The extra work increases myocardial tissue oxygen demands and augments the cycle started by the ischemic heart.
Answer to Question 2
A, C, D, F
Standard HF therapy includes taking medications as prescribed with a low-sodium diet to control total body fluids. Usually, dyspnea in a patient with HF is due to hypervolemia, which occurs after a lapse in adherence to the standard HF therapy. The nurse checks the patient's extremities for edema because peripheral edema is a clinical indicator of hypervolemia. If the patient is nonadherent with therapy, then the nurse is more likely to find peripheral edema than with an adherent patient. Hypervolemia can also be due to worsening HF. The nurse listens to the pa-tient's lungs to assess for pulmonary edema as a cause for the patient's dyspnea. Pulmonary edema can be caused by hypervolemia from nonadherence to therapy or from worsening HF. The nurse compares the patient's weight to his baseline to determine whether the patient has expe-rienced a sudden weight gain, which would be indicative of hypervolemia. Assessing the pa-tient's diet over the last 48 hours can provide clues about a potential cause of the patient's dysp-nea. If the patient increases the dietary sodium by eating pizza, pickles, and processed food, among others, the patient is likely to experience a sudden increase in total body fluid, which can cause the patient's dyspnea.
Although older adults with HF complain of anorexia, bowel habits are not as likely to be affected by hypervolemia as is the appetite. Coughing is a nonspecific, nonsensitive indicator of pulmonary edema.