|
|
|
Did you know?
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system destroys its own healthy tissues. When this occurs, white blood cells cannot distinguish between pathogens and normal cells.
Did you know?
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.
Did you know?
Hyperthyroidism leads to an increased rate of metabolism and affects about 1% of women but only 0.1% of men. For most people, this increased metabolic rate causes the thyroid gland to become enlarged (known as a goiter).
Did you know?
If you use artificial sweeteners, such as cyclamates, your eyes may be more sensitive to light. Other factors that will make your eyes more sensitive to light include use of antibiotics, oral contraceptives, hypertension medications, diuretics, and antidiabetic medications.
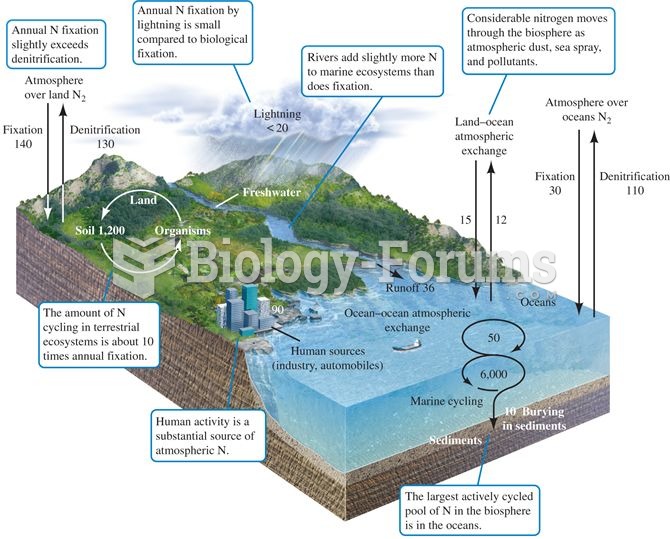 The nitrogen cycle. Numbers represent fluxes as 1012 g N per year (data from Schlesinger 1991, after
The nitrogen cycle. Numbers represent fluxes as 1012 g N per year (data from Schlesinger 1991, after
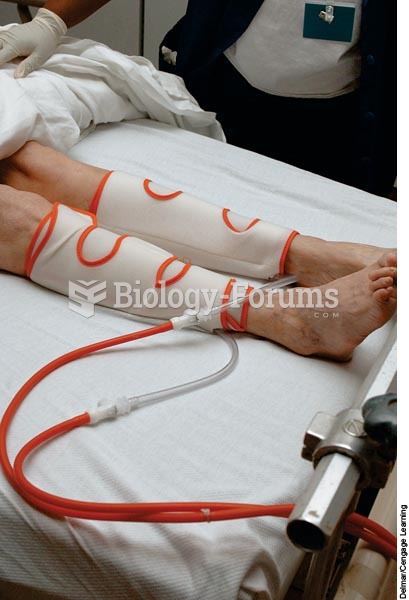 An alternating pneumatic compression device squeezes the leg tissues causing blood to move toward th
An alternating pneumatic compression device squeezes the leg tissues causing blood to move toward th
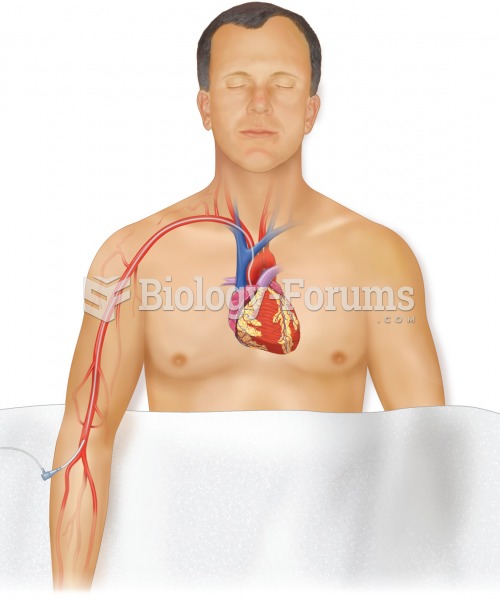 Cardiac catheterization. Insertion of a tube called a catheter through a blood vessel. In this examp
Cardiac catheterization. Insertion of a tube called a catheter through a blood vessel. In this examp