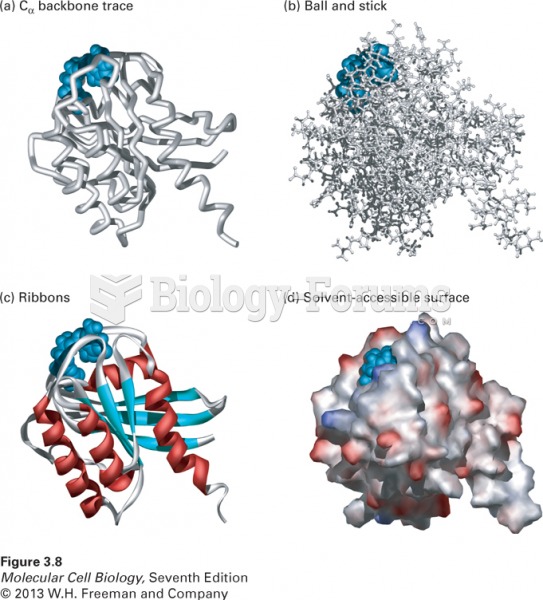
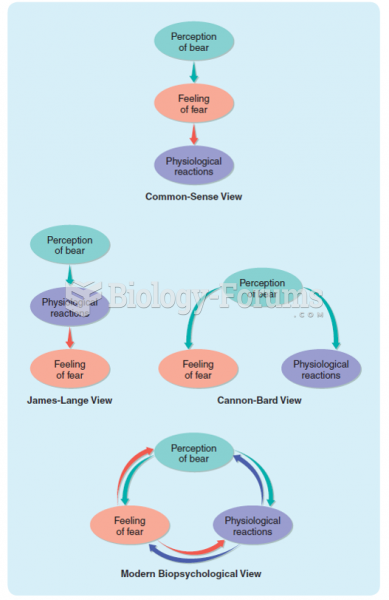
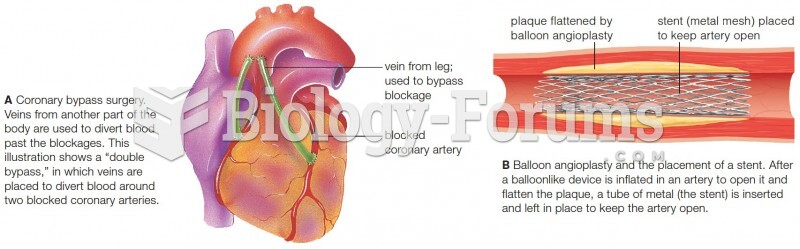
|
|
|
The most destructive flu epidemic of all times in recorded history occurred in 1918, with approximately 20 million deaths worldwide.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
Parkinson's disease is both chronic and progressive. This means that it persists over a long period of time and that its symptoms grow worse over time.